



ORLANDO, FL — April 29, 2025 Battcon, organized by the Consortium for Battery Innovation (CBI), is the industry’s benchmark event for real-world application training and the latest critical developments in stationary battery systems. Today, Battcon announced that the IEEE Power & Energy Society (PES) will be the technical co-sponsor for its 2025 event. This marks the first technical co-sponsorship between Battcon and the IEEE Power & Energy Society, expanding the conference’s global reach and technical impact.
Scheduled for Aug. 3–6, 2025, in Orlando, Florida, Battcon brings together engineers, operators, manufacturers and end users to address critical challenges in backup power systems for many different markets like data centers, energy storage systems, utilities, and telecommunications. With IEEE PES involvement, Battcon 2025 will be included on the IEEE Conference Search/Call for Papers website, and conference materials will be eligible for archival in IEEE Xplore®, expanding access to speaker research and technical findings across the global energy community.
“The involvement of IEEE PES as a technical co-sponsor enhances the already outstanding technical content at Battcon 2025,” said Dr. Matt Raiford, senior technical director of the Consortium for Battery Innovation. “Their role in co-publishing and archiving the conference’s peer-reviewed technical papers ensures that our speakers’ contributions are preserved and shared with a global network of power and energy professionals. This partnership strengthens the value of Battcon as a platform for advancing real-world battery applications in critical infrastructure.”

The IEEE Power & Energy Society, the world’s leading forum for electric power and energy innovation, has more than 42,000 members worldwide. Their participation furthers Battcon’s mission to deliver top-tier technical education and drive advancements across grid storage, telecom backup and data center UPS systems.
Battcon, organized by the Consortium for Battery Innovation (CBI), is where technical expertise meets real-world application. The 2025 event will feature expert-led sessions, pre- and post-conference workshops, an expanded expo, and targeted networking receptions connecting professionals across the stationary battery community. In Battcon’s uniquely independent exhibit hall, attendees can engage directly with leading manufacturers, suppliers and service providers. Learn more at www.battcon.com.
The LDES Consortium is a compelling initiative focused on advancing long-duration energy storage (LDES) technologies to enhance grid reliability and support the integration of renewable energy. In this interview, Dr. Alyssa McQuilling, CBI's Research & Innovation Manager, provides insights into the consortium's goals, the roles of its members, and the innovative solutions to push the boundaries of energy storage.
Can you give us a brief overview of the LDES Consortium and its primary goals?
Sure! The LDES Consortium is an exciting initiative that brings together diverse stakeholders to tackle the challenges of long-duration energy storage (LDES). The main aim is to overcome both technological and economic barriers to make LDES more viable and widespread.
What makes this consortium special is that it's 'technology agnostic ', meaning we're not biased towards any specific energy storage technology. We have experts from different energy storage technologies, such as chemical, mechanical, thermal, and all types of batteries, including lead and lithium. The idea is to address every aspect of the industry, from developing the workforce and managing the supply chain to creating policies and advancing technology, regardless of the specific technology used.
What roles do you and Dr. Matt Raiford, CBI's Technical Director, play within the LDES Consortium, and what are the 'tiger teams' you're involved with?
Matt and I are involved in several 'tiger teams' within the consortium. These teams are focused groups that tackle specific challenges related to long duration energy storage. Each team is dedicated to addressing a unique aspect of the LDES landscape.
Between the two of us, we're active in about eight tiger teams, where we attend meetings, provide feedback, and help refine the challenges and recommendations alongside other industry experts.
Uniting experts for energy innovation
How does LDES differ from other types of energy storage, and why is it important?
That's a great question. LDES stands out because it can store energy for more than ten hours, which is crucial for ensuring the grid's reliability. Some technologies are perfect for shorter durations, while others can handle much longer storage times, even up to seasonal storage.
This capability is especially important as we integrate more renewable energy, which can be unpredictable, into the grid. In simple terms, LDES helps balance supply and demand, ensuring enough energy is available when it's needed the most. This makes it a key player in creating a stable and sustainable energy system.
You're leading the Workforce Development team. What does that entail, and why is it crucial for the project?
I'm the industry advisor for the Workforce Development team, which is led by Hope Corsair at Oak Ridge National Lab. Our team's mission is to determine what skills and training are needed to build a strong workforce for the LDES industry. We've examined current workforce needs and are making recommendations to help scale the industry and prepare for future demands.
This builds on my previous work with the NAATBatt Education Subcommittee, where we focused on the educational needs of the battery industry. Ensuring we have a skilled workforce is essential for the success of LDES technologies.

What are some of the big challenges you face in making LDES more common, and how are you addressing them?
One of the biggest challenges we face is the cost. For instance, the current systems are primarily designed for shorter durations, making them less cost-effective for longer storage needs. Another challenge is scaling up the supply chain for these newer technologies, which haven't been widely deployed yet.
To address these, we're working on creating new market structures and incentives for long-duration energy storage. We're also confident that as the industry gains more experience, costs will come down, and these technologies will become more affordable.
Can you share a success story or milestone the LDES Consortium has achieved so far?
Absolutely! One of our early successes has been the release of initial recommendations from our tiger teams. These drafts are currently under review and will help guide the consortium's future activities.
We're also planning our first in-person consortium meeting in September in California, which is expected to bring together up to 300 attendees. It's a great opportunity to build momentum and collaboration.
Building a sustainable energy ecosystem
Sustainability and environmental impact are critical concerns. How do these advanced energy storage solutions help create a greener and more sustainable future?
LDES is crucial for maintaining grid reliability as we increase the use of renewable energy sources. By storing energy for longer periods, LDES helps balance the intermittency of resources like wind and solar. Technologies like lead batteries provide long duration storage and have established recycling processes, supporting a more sustainable energy ecosystem.
What potential do LDES technologies hold for transforming the energy landscape in developed and developing regions?
LDES has the potential to improve how we use renewable energy by making it more reliable and accessible. It can be integrated into large national grids as well as smaller microgrids, which are particularly beneficial in developing regions. This flexibility can support broader electrification and sustainable development goals globally.
Looking ahead, what impact do you think LDES will have on our everyday lives and the global energy landscape?
I believe that LDES will become a seamless part of our power grid, supporting decarbonization and electrification efforts. It will ensure we have reliable power whenever it's needed, helping to make our energy systems more resilient and sustainable.
It will be interesting to see the development of new technologies and the lessons we can learn from existing ones to ensure that the industry's growth is sustainable. This starts from the extraction of raw materials, through manufacturing and the lifetime of the systems, all the way to the end of life and recycling/materials recovery.
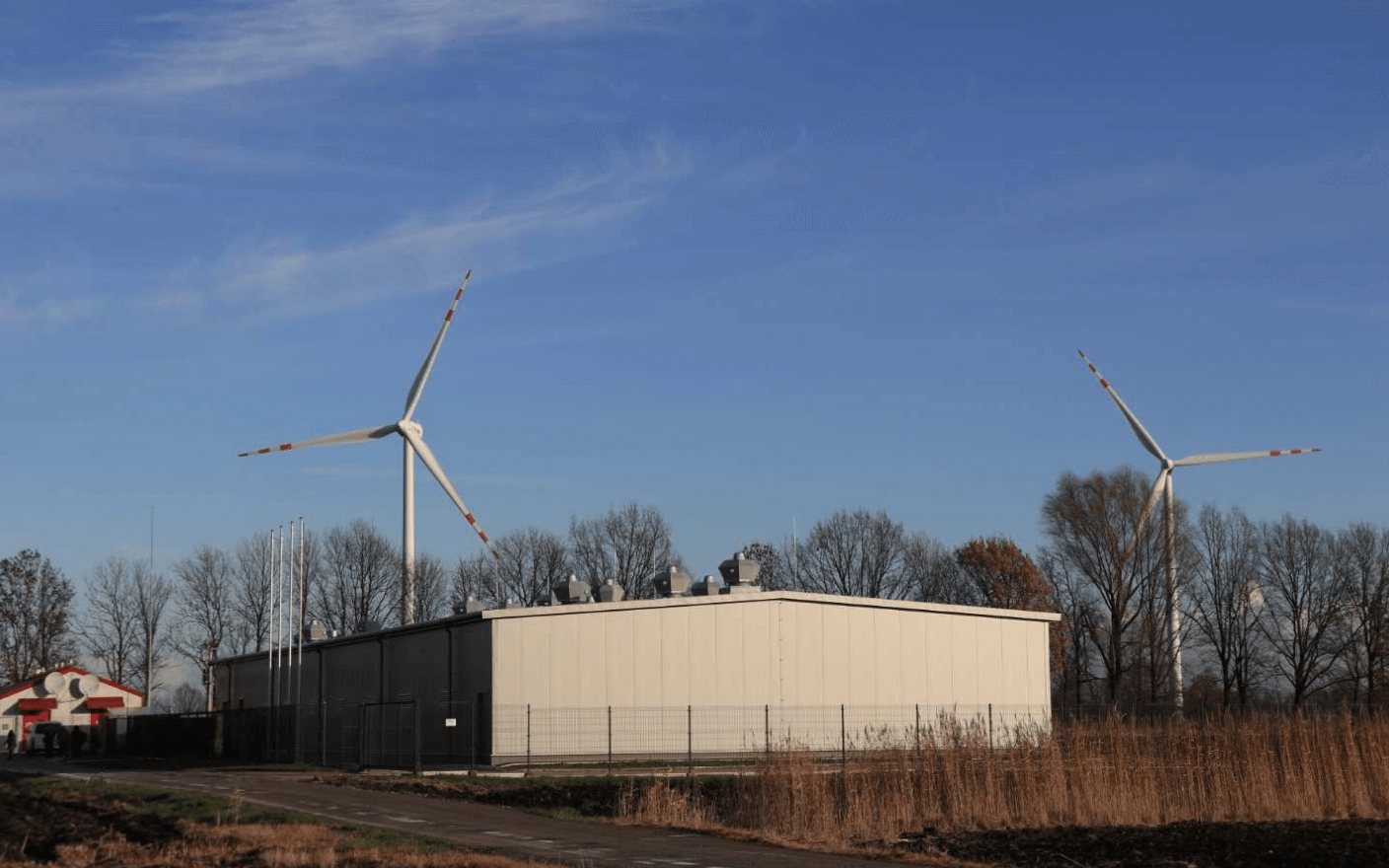
This hybrid energy storage (ESS) system made of advanced lead and lithium batteries is currently the largest of its kind in Poland.
Strategically situated to enhance the Bystra Wind Farm in Northern Poland, this facility maximizes renewable energy usage and stabilize local energy supplies.
Through efficient energy time-shifting, the system provides a reliable power source during peak demand periods, lowering energy costs for industries and residents. It focuses on low-carbon technologies and high recycling rates, setting a new standard for energy solutions in the region.
| Location | Gdańsk County, Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland |
| Project launch | October 2019 |
| Construction time | 12 months |
| Size of the system | advanced lead batteries: 26.9 MWh energy; 5 MW power | lithium batteries: 0.47 MWh energy; 1 MW power; 4.5-hour system |
| Battery type | 2 V advanced lead-carbon AGM batteries** and lithium batteries |
| Battery provider | Showa Denko Materials |

View CBI's Interactive Map of energy storage case studies
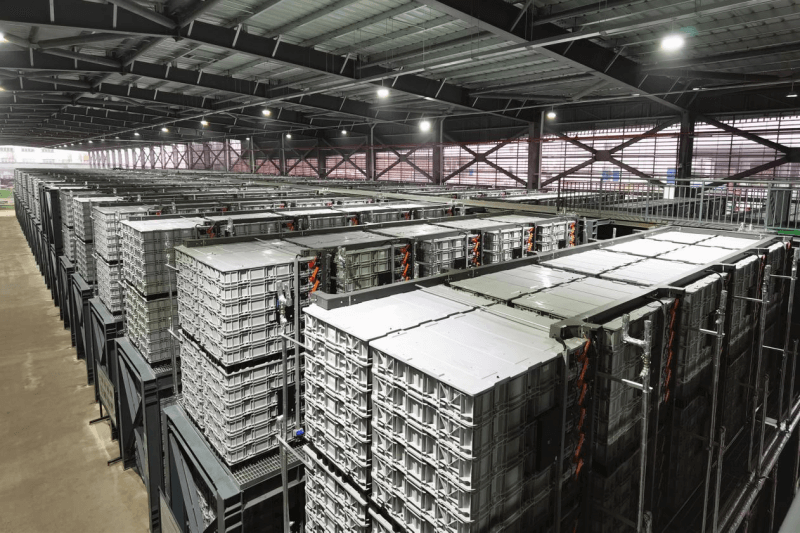
This long-duration energy storage (LDES) system made of advanced lead-carbon batteries is currently the largest of its kind in the world.
Connected to Huzhou's main electricity grid since March 2023, the installation is helping to reduce energy costs to industries and citizens by providing an alternative power source at peak rates. These systems bring significant advantages such as low investment cost and rapid return on investment, and low carbon footprint with long design life and material with high recycling rates.
| Location | Huzhou, Zhejiang Province, China |
| Project launch | March 2023 |
| Construction time | 3 months |
| Size of the system | 1000 MWh (1 GWh) energy, 100 MW power; 10 hour system |
| Battery type | 3 million 2 V advanced lead-carbon AGM batteries |
| Battery provider | batteries were made in China, by Tianneng Power |

View CBI's Interactive Map of energy storage case studies
We live in an era when smart homes have become part of our everyday lives and energy storage systems are changing the way we think about energy.
Growing up, many of us were captivated by the portrayal of modern and futuristic homes on television. Each depiction was unique, yet they all shared a common charm—a certain "wow" factor that held our gaze, sparking imagination about the endless possibilities technology could bring to the future. Although we may not have parking spots for family spaceships in our backyards just yet, the vision of the future we once admired is closer to reality than we might think.
Today, we live in an era when smart homes have become part of our everyday lives. Our houses now integrate various inventions, all harmoniously working together. By integrating smart technologies that make our homes more energy efficient, we're taking steps towards preserving our planet and addressing the ongoing climate crisis.
Technology meets sustainability
An example of such smart technology is a battery energy storage system. This modern yet increasingly common technology enables us to capture and store energy for later use, marking a shift in how we power our homes. This article takes you on a journey through the modern home, exploring practical and innovative uses of energy storage systems. Transforming what may once have appeared as science fiction into part of the solution for a greener, more sustainable lifestyle, energy storage systems are changing the way we think about energy.

The tour already begins outside the house, where the renewable energy narrative forms under the open sky. Solar panels, discreetly placed on the roof, capture and convert the sun's warmth. This stored energy then finds its way back into the house, supplying hot water for daily use or heating indoor spaces, making every drop of sunlight count. This highlights how sustainability and modern living go hand in hand, showing that even our garden can play a role in powering the home.
As we enter the house and step into the living room, the last rays of daylight fade into the soothing glow of several desk lamps, all backed up by energy stored from today's sunshine. The television, gaming consoles, and even the WiFi router sip electricity from the reservoir of clean energy. This seamless integration of energy storage systems allows us to relax in front of the television after a long day or cosy up on the sofa with a favourite novel under the warm light of the lamp without giving a moment's thought to outside energy constraints.
Smart energy in action
Moving into the kitchen, the narrative of energy efficiency continues. Here, everyday activities continue as usual but with a green twist. Appliances, backed up by an innovative energy storage system, manage power usage with precision. The refrigerator hums quietly to keep the food fresh while the oven preheats for dinner, and the dishwasher stands ready, all running on stored energy. The effortless way the kitchen incorporates and utilises stored energy highlights the real-life benefits of energy storage systems, seamlessly blending functionality and sustainability.
Moving further into the house, we find ourselves in the utility area. Here, the air thrums with the quiet power of energy storage systems, balancing the home's temperature through a clever heat pump paired with batteries. These systems allow solar energy to efficiently power the heat pump, which can then be used to keep the house warm or provide hot water, even long after the sun has set.

Heading to the garage, the connection between energy management and mobility can be seen in action. An electric vehicle has become an essential part of the home's energy system, quietly charging and preparing for its next journey. Here, the vehicle-to-home power-sharing concept comes to life, allowing energy to flow back into the house during peak times or unexpected outages.
Green future with energy storage
Concluding the journey through the house, we can see energy storage systems integrated into our daily routines as a glimpse into a more sustainable future. From the warm comfort of the living room through the bustling kitchen and out into the garden, we see a snapshot of what could become the norm.
As the European Union strides towards a greener future with initiatives such as the Green Deal, homes equipped with battery energy storage systems are helping us get closer to energy independence. The battery energy storage market is predicted to grow significantly, and all battery technologies will play an important role. In light of the pressing need for climate action, these systems represent vital components of sustainable living and a greener, technologically advanced world.
LoCEL-H2, a four-year initiative, is bringing innovative energy solutions to remote communities in Africa. In this interview, Dr. Athanasia-Maria Tompolidi, CBI's Research & Innovation Manager, discusses the project's goals, technological innovations, and commitment to community empowerment.
Let's start with the basics. Can you tell us what the LoCEL-H2 project is about and what it aims to achieve?
Of course. LoCEL-H2 is an innovative, four-year project under Horizon Europe that kicked-off in January 2023. It aims to bring scalable microgrid systems to isolated communities. These communities often lack steady access to energy like electricity and clean cooking facilities, which is taken for granted in the developed countries.
We combine solar power, advanced lead battery systems, and green hydrogen technology to offer sustainable and affordable energy solutions. And it is not just about technology. Empowering women in these communities is a big part of our project, especially in places like Zambia and Ivory Coast. We have an amazing team of partners from all over the globe, bringing diverse expertise to the table.
In a world teeming with green innovations and an urgent need for sustainable solutions, what sets LoCEL-H2 apart from the crowd, and why is it particularly crucial now?
LoCEL-H2 uniquely intertwines new technology with Social Sciences and Humanities (SSH) insights, hitting that crucial spot where technical solutions meet community needs head-on. We are in sync with the EU's hydrogen strategy and REPowerEU plan, introducing innovative ways for decarbonisation and independence from fossil fuels. By introducing green hydrogen solutions in developing countries, LoCEL-H2 contributes to global decarbonisation efforts and supports the European Green Deal's objectives.
Given the challenges posed by climate change, especially for vulnerable countries, projects like LoCEL-H2 provide essential tools for Climate Adaptation. It addresses critical issues such as food security, water supply, education, disasters risk reduction and public health.

From sunlight to energy storage
Innovation is key to the project. Could you explain how green hydrogen and advanced lead batteries work and why they're game-changers?
LoCEL-H2 stands on three innovation pillars. The first is a scalable, plug-and-play microgrid that uses solar energy to power communities. The second is a battery energy storage system tailored for households, small businesses, and community infrastructures to ensure a steady energy supply. The highlight is our community-shared battery-electrolyser, a novel system for energy storage and green hydrogen production.
Our vision with LoCEL-H2 is simple: we want to re-power the communities, quite literally. These smart innovations contribute to tackling energy poverty and provide sustainable solutions for those lacking access to reliable energy.
Could you give us an update on how the project is progressing and any significant milestones you've hit so far?
This past year has been remarkable. LoCEL-H2 has made significant progress thanks to our team's hard work and collaboration. We have mapped out stakeholder databases across continents. Our team has visited African and Pakistani villages to learn more about the communities and their energy needs. Key technical milestones of the project include the strategic design of our battery-electrolyser and advancements in energy storage solutions.
Our team has been meeting regularly, both online and in person, to ensure we stay on track. We had a face-to-face General Assembly in Naples in the autumn of 2023 and are looking forward to the upcoming one in Brilon, Germany, in the spring of 2024. It is very reviving to keep the in-person interaction.
Communities thriving on clean energy
Everyone's excited to see results. What are the short-term and long-term benefits LoCEL-H2 brings to the table?
LoCEL-H2 aims to change the way we access energy while promoting social and economic growth. Our focus is on innovative microgrid technology that combines battery-electrolyser and advanced lead battery energy storage to meet the unique needs of communities.
In short term, our goal is to empower communities by providing them with education and training on how to manage and benefit from these energy systems. We are working closely with people on site to ensure they are not just recipients but active players. This approach helps to create job opportunities and stimulate local economies.
In long term, we envision these efforts blossoming into sustainable, self-sufficient communities thriving on renewable energy. By introducing this technology, we're also helping to position the EU as a leader in clean energy innovation, supporting the green energy transition.

Beyond energy access, how does the project aim to influence societal change, for example?
At the heart of LoCEL-H2 is a deep commitment to societal change, particularly through empowering women in some of the world's most vulnerable areas.
We aim to see these women replacing old, smoky stoves with clean, green hydrogen, stepping into new roles, and changing the game in their communities. Our goal is to give them the time and resources they need to engage in social activities, achieve financial independence and be in charge of their own lives.
Moreover, with cleaner cooking, we are looking towards a greener future for them and the entire planet. It's a big vision, but with every step, we're closer to making it a reality.
Energy equity for sustainable future
Looking ahead, how do you plan to expand the reach of LoCEL-H2 to empower more communities worldwide?
Our aim for the future is to expand the impact of LoCEL-H2 beyond the current scope. We are working on integrating renewable energy into the very fabric of communities in need. This is particularly important when the world faces high energy demands and climate concerns, and sustainable solutions are needed more than ever.
Aligned with the EU's strategic priorities to mitigate climate change, LoCEL-H2 is committed to supporting the transition towards green energy across the globe, with a special focus on Africa, where the need is most acute. This can be achieved with collaborations with initiatives like Energising Africa and the Clean Cooking Manifesto. Increasing access to clean cooking is a topic that has been high on the global climate agenda, for example in the last United Nations Climate Change Conference COP28, and LoCEL-H2's technology is particularly well suited to be part of the solution.
Our approach is about connecting, sharing, and collective learning, which we believe to be some of the most valuable aspects of the project. We are sparking a movement through interactive webinars, training sessions, and collaboration with sister projects under Horizon Europe.
So, when discussing what's next for LoCEL-H2, it's all about showing that energy equity and a sustainable future are possible. LoCEL-H2 is dedicated to providing access to clean, green energy to communities worldwide. Its mission is to empower, inspire, and support the adoption of sustainable living practices worldwide.
Uncovering the key role of energy storage in Europe's green revolution
As we step into a new year marked by record-breaking temperatures, the urgency to address climate change intensifies. A recent analysis has confirmed 2023 as the warmest year on record, with over 200 days setting new daily temperature records.
It is crucial that cities join the shared drive to mitigate the climate crisis and transition to greener, more sustainable energy. This was emphasised at COP28, where fossil fuels were officially recognised as the primary cause of climate change for the first time after 28 years. Within Europe, the European Commission is leading the way by introducing ambitious initiatives such as the Fit for 55 package and Effort Sharing Regulation to shift towards a low-carbon economy. These initiatives have sparked innovation and collaboration among European cities as they strive to embrace a more sustainable path.
The second part of our series on sustainable cities highlights the transformative efforts of three European cities – Helsinki, Ljubljana, and Sofia – in embracing energy storage to spearhead their sustainability goals. These cities serve as examples of how local governments can initiate a transition towards renewable energy, sustainable transportation, and emission reduction.

Embracing sustainable energy solutions
In the northern part of Europe, Helsinki is a pioneer in sustainability. The Finnish capital has embraced energy storage as a key element in achieving its goal of carbon neutrality by 2030. The city has launched an inventive project in collaboration with its energy provider to integrate battery energy storage into electric vehicle charging stations. The initiative taps into the potential of electric vehicles as mobile energy storage units, capable of storing excess energy generated from renewable sources. This energy can power the vehicles or be returned to the grid, making the energy ecosystem more connected and resilient.
According to the city's mayor, Juhana Vartianten, building a sustainable future is the most pressing issue we face today. "Helsinki wants to encourage cities around the world to embrace sustainability work and take concrete action. The coming years will determine the direction humanity takes, " said Vartiainen in the 2023 Voluntary Local Review, "That is why we must act now, and we must act together. We still have a long way to go, but fortunately, we are heading in the right direction."
Sofia, the vibrant capital of Bulgaria, is another city that has made sustainability a cornerstone of its urban development strategy. The city has implemented a number of innovative projects that are helping to reduce its reliance on fossil fuels and improve energy efficiency.
One of Sofia's most notable initiatives involves the installation of intelligent batteries throughout the city's public transportation network. These batteries act as mobile energy storage units, allowing buses and trams to store energy while braking or coasting downhill. The captured energy can then power the vehicles as they climb uphill or accelerate. This approach has shown promising results during its trial phase, with an expected 10-15% reduction in fuel usage and a 30% decrease in harmful carbon emissions, contributing to cleaner air and a more sustainable transportation system.
In addition to the environmental benefits, Sofia's battery storage project also streamlines the public transportation system, reducing the need for frequent recharging. The batteries provide a clean source of energy that can be used during peak hours, allowing passengers to rely on a more efficient public transportation system.

Harnessing the power of energy storage
Ljubljana, the capital of Slovenia, is known for its eco-friendliness and sustainable urban development. The city is taking steps to make its buildings sustainable while preserving its rich cultural heritage. One way Ljubljana is achieving this balance is by implementing energy storage systems in public buildings and infrastructure. The Ljubljana City Hall is equipped with a battery storage system that can store energy from the sun. Moreover, Ljubljana aims to expand its energy-saving efforts beyond City Hall by installing energy storage systems in public buildings such as schools, libraries, and other facilities.
Integrating energy storage systems into public buildings is a win-win solution for both cities and citizens. By doing so, the city enhances energy security, lowers energy expenses, and provides backup power during grid outages. This not only reduces the city's environmental footprint, but also provides its citizens with reliable access to energy.
In a world where climate change looms, Helsinki, Ljubljana, and Sofia are examples of how innovation and energy storage can shape a sustainable future. These cities have set the bar high by adopting measures that align with the EU's Green Deal goals, aiming to reduce carbon emissions and switch to renewable energy sources.
Helsinki's electric vehicle charging stations, Ljubljana's public buildings integrated with battery systems, and Sofia's intelligent battery storage for public transportation all show how technology can help create a cleaner, more resilient planet. By reducing carbon emissions and embracing renewable energy sources, these cities are leading the way in the fight against climate change.
Batteries are a fundamental driver of the green energy revolution. It is estimated that our society’s energy needs represent over 70% of all carbon emissions, with the largest shares coming from electricity and heat sources and transportation systems. The push to achieve net-zero is evident from numerous governmental initiatives such as the EU's commitment to cut carbon emissions by more than half by 2030, and global pacts such as the recent COP28 deliberations. To reach these goals means to effectively decarbonise the energy sector, and batteries will support the rollout of renewable energy infrastructure by providing energy storage capacity and reduce transport-related emissions by powering electric vehicles.
Batteries in energy markets are currently dominated by lithium-ion technology, but their employment in electric vehicles is given priority due to this technology’s unrivalled properties for this end use. This opens space for different technologies in other applications. Energy storage is a notable example, with battery energy storage capacity expected to grow twentyfold by 2030. All viable battery technologies will be needed to fulfil this soaring demand, and research & innovation to improve consolidated technologies is identified as an important way forward.
Lead batteries are currently the only other technology with well-established manufacturing and recycling infrastructure across the globe. But even if today's advanced lead batteries have come a long way from classic lead-acid car batteries in terms of overall performance, there are still various pathways for further improvements being discovered and explored.
The Consortium for Battery Innovation (CBI) is the only global lead battery pre-competitive research organisation. Our goals are to help deliver the advanced lead batteries needed for the energy transition and to demonstrate their power to bring real change. We do so by assessing market needs to define concrete research goals, by providing financial support to breakthrough projects through our Technical Program, and by establishing partnerships to develop pioneering advanced lead battery-based solutions.
In this overview, we discuss how some of our projects are paving the way to unlock the full potential of advanced lead batteries for the green energy transition.
The indispensable low-voltage ally
Electric vehicles are key for a decarbonised transport. As the nonstop evolution in automotive technology requires more and more from the main lithium-ion battery, smaller auxiliary batteries, also called low-voltage EV batteries, have been increasingly employed for safety back-up and supply power to specific electronic features. This means advanced lead batteries can work alongside lithium-ion batteries to ensure our future decarbonised road transport fleet is also safe.
CBI’s Technical Program has been supporting projects focused on automotive lead battery optimisation for start-stop, microhybrid and auxiliary use. Some encouraging results include improvements in the methodology of laboratory cell testing to investigate key parameters for automotive applications, and valuable insights on the role of additive formulations to enhance automotive battery performance. Ongoing studies, such as the investigation of microscopic changes in positive and negative electrodes during different charge conditions, along with future projects, will continue to provide guidance for better active material formulation and performance metrics.

Taking energy storage capability to the next level
The shift to renewable energy is just getting started, and more extensive rollout will be closely followed by a sharp increase in the need for energy storage systems to compensate for the intermittent nature of these energy sources. Global performance targets are aggressive and require different battery technologies with long lifetimes, high total energy throughput and low acquisition cost to meet technoeconomic needs. Our industry is focused on delivering longer lasting and more energy dense batteries to help meet the demand for utility, commercial, residential, and industrial energy storage applications.
Different projects supported by CBI’s Technical Program have been investigating advanced lead battery enhancements specifically for energy storage applications. Key findings so far include insights into barium sulphate additive configurations that can bring benefits to overall cycle life, and in-situ analyses during battery operation to understand charge and discharge processes and their products. More exciting results will come from projects and initiatives starting in 2024, including CBI’s involvement in the U.S. National Consortium for the Advancement of Long Duration Energy Storage Technologies. This will keep adding to our growing knowledge base and contributing to advanced lead battery performance improvement for energy storage.
Powering a just transition
The lack of access to both electricity and clean cooking, known as energy poverty, remains a pressing global issue. It is estimated that 775 million people lack access to electricity and 2.2 billion people lack access to clean cooking fuels, mostly in Sub-Saharan Africa and developing Asia. Providing universal clean energy access leaving no one behind is essential for a successful green energy transition. But the rollout of renewable energy in areas with no or incipient grid infrastructure is challenging, and lowering investment costs is a must. Through ongoing partnerships, we are demonstrating that the combination of microgrids and advanced lead battery storage is an excellent solution to provide clean and affordable energy for remote communities.
In an ongoing initiative funded by Horizon Europe, we are helping to develop a deployable clean energy solution with provision of electricity through prosumer-based solar microgrid coupled with an energy storage system made of advanced lead batteries. One core innovation in this battery energy storage system is the addition of an electrolyser to produce green hydrogen, which can be used as clean cooking fuel. By the end of the project in 2026, the team will deploy two full-scale pilots of this pioneering energy solution, one in Côte d'Ivoire and one in Zambia.
CBI is also contributing to another smart solution, this one already in testing phase: a solar energy microgrid with a combined micro electric tractor. Advanced lead batteries power both the microgrid energy storage system and the tractor. The project, funded by Innovate UK, aims to bring a 2-in-1 solution for rural communities by providing clean energy and optimising land preparation. Recent field demonstrations have shown the potential of the micro electric tractor to significantly increase crop yields, which will help to increase smallholder incomes. The solution has been selected as one of the finalists of a prestigious international green energy prize.
Novel solutions like these not only alleviate energy poverty issues but also provide a pathway toward citizen empowerment. They can substantially contribute to universal access to modern energy and to achieve other Sustainable Development Goals regarding poverty reduction, health and education.

This is why we believe the future is bright and green and we will continue to drive advanced lead battery innovation for sustainable development and a climate-resilient future.
Our colleagues Matt Raiford, CBI's Senior Technical Manager, and Alyssa McQuilling, CBI's Research and Innovation Manager, were featured in the latest Beyond Lithium podcast episode hosted by Nate Kirchhofer from BioZen Batteries. The discussion revolved around the work of CBI, research and innovations driving the industry, exciting new projects, unique features of advanced lead batteries and the future of energy storage.
CBI's projects and mission
Matt kicks off the conversation by outlining CBI's mission as a pre-competitive global research organisation with over 130 members worldwide. According to Matt, the priority of pre-competitive research lies in CBI's focus on applications and innovations benefiting the entire lead battery industry. "It's like taking a step back and looking at first principles," Nate summarises, as both guests noted.
The conversation reveals CBI's projects, showcasing an advanced lead battery technology for different applications. Matt and Alyssa shed light on CBI's involvement in global government funding opportunities, with recent projects spanning Europe and the UK. Alyssa introduces the current LoCEL-H2 project, featuring the unique battery-electrolyser. The technology stores energy to produce electricity on demand and utilises initially unwanted side reactions to produce hydrogen for cooking purposes. Another noteworthy project, Aftrak, showcases a solar advanced lead battery-powered tractor for deep-farming piloted in Africa. "These projects highlight something really important about batteries in general, that they can enable a whole new way of living," noted Matt.
A closer look at lead batteries
The podcast takes a turn as the team delves into the chemistry of lead batteries. "Lead batteries have been around for a hundred years, and they've been doing a lot of work," Nate acknowledges, addressing the never-ending question of getting people excited about lead. Dispelling misconceptions around lead batteries, Matt and Alyssa passionately discuss their unique benefits, including sustainability, an increasingly relevant factor in today's society. "Lead is the most recyclable product in the world," Matt emphasises, "This results in a recycling rate of over 99% in the US and Europe."
Energy storage takes centre stage in the conversation, as it has been emerging prominently in political dialogues worldwide. According to Matt, the performance rate of lead batteries is the main driver for energy storage. First invented in a French man's backyard, lead batteries evolved drastically into well-adapted products. As a scientist, Matt wondered how this technology didn't advance when he came across it years ago. The explanation is simple: there was no market driver. Nowadays, there is one. "That's what we're doing at the CBI. A lot of our research is inspired by the needs of the market," Matt explains.
The future of energy storage
"We need a lot of energy storage integrated into the grid as we decarbonise and electrify more," Alyssa states, touching on the need for diverse technologies to meet the escalating need for clean energy. This offers countless opportunities across sectors. The demand for energy storage and battery innovations go hand in hand. Improvements in cycle life and battery materials are a few examples of research in national labs, where new technologies and techniques are involved to better understand batteries at a fundamental level.
The podcast concludes with a forward-looking perspective on the future of energy storage. The energy storage sector's scale and pace of development promise a huge demand for batteries. "We see a steady growth for lead. For energy storage, the sky's a limit. We're talking about terawatt-hours batteries needed by 2030," Matt says, highlighting the increasing need for diverse technologies to coexist harmoniously. "We just have to create a cheap battery that lasts a long time," he concludes with a smile.
A special thanks to our colleagues, Matt Raiford and Alyssa McQuilling, for this insightful conversation, showcasing the work at CBI and providing valuable insights into the role of lead batteries in shaping a sustainable and energy-efficient future. Listen to the full podcast on the Beyond Lithium website.
The COP28 conference marked an important moment in the global conversation about energy storage and batteries. While signalling the need to move away from fossil fuels, it emphasised the potential of energy storage to shape a sustainable energy future significantly.
The 28th Conference of the Parties (COP28) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change was held in Dubai from 30th November to 12th December. The conference brought together global leaders, experts, and stakeholders to address the pressing issue of climate change. The theme of COP28 was "Building a Resilient Future," focusing on accelerating global action to limit global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels.
Despite the scepticism that preceded the conference, particularly surrounding the host nation, Dubai, a major oil producer, COP28 emerged as a revolutionary climate change summit. For the first time in 28 years, fossil fuels were formally recognised as the primary driver of climate change. This acknowledgement, a significant shift from the previous COPs, marked a turning point in the international community’s approach to climate change. It challenged the long-held narrative that fossil fuels were necessary for the energy mix and laid the foundation for a faster transition to a low-carbon economy. This formal recognition of fossil fuels’ role in climate change was not just a symbolic gesture but led to a series of bold decisions and commitments to accelerate the global transition to clean energy sources. Over 100 countries pledged to phase-out coal power by 2030, which is a huge milestone in decarbonising the energy sector.

Energy storage for green transition
COP28 provided an opportunity for stakeholders to discuss the complexities of energy storage technologies and their potential to contribute to a more sustainable energy future. The discussions focused on integrating renewable energy sources, enhancing the stability of power grids, and addressing the issue of energy poverty. COP28 witnessed several notable developments related to energy storage, including the launch of the Supercharging Battery Storage Initiative and the Multilateral Consortium for Battery Storage.
Member governments of the Clean Energy Ministerial (CEM), including the European Commission, Australia, Canada, and the United States, announced the launch of the Supercharging Battery Storage Initiative in Dubai. This initiative aims to increase the capacity of battery storage in the power grid while ensuring a transparent, resilient, and sustainable energy system. It is focused on reducing technology costs, as batteries play a crucial role in creating a flexible and reliable energy system. Through this initiative, member governments of the CEM are committed to a cleaner and more accessible energy future. “Battery storage will be the backbone of the green transition with an essential role in decarbonising transport and energy. It will enable a truly decentralised and integrated energy system based on efficient use and renewable generation,” said Maroš Šefčovič, Vice President of the European Commission.
Bridging the energy gap
The Global Leadership Council announced the formation of the Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) Consortium, with participation from 11 African countries. The consortium has pledged to deploy a minimum of 5GW of battery storage systems in Africa by 2030. The initiative seeks to tackle energy poverty and improve access to reliable electricity in low- and middle-income nations on the continent. Dr. Rajiv J. Shah, the President of The Rockefeller Foundation and Co-chair of the GLC, highlighted the need for transformative initiatives. He stated that "Without sufficient storage capacity, countries will be unable to add renewable energy to their grids at the scale needed to reduce emissions and create economic opportunity. The BESS Consortium is an example of the sort of big, bold action required to break down the barriers that are preventing people and communities from joining the ongoing climate transformations."

As part of the COP28 agreements on energy storage, the United States and partner countries of the Net Zero World initiative have announced significant progress in building clean and secure energy systems in emerging economies. This includes helping Ukraine deploy distributed renewable energy and storage systems for critical infrastructure. Participants of COP28 have also called for increased investment in research and development for energy storage technologies. The aim is to accelerate innovation, improve performance, and reduce costs, making energy storage more accessible and cost-effective.
Advancing a cleaner future
The decisions and commitments made at COP28 are a step forward in the global effort to combat climate change. By acknowledging the role of fossil fuels in climate change and committing to a rapid transition towards a low-carbon economy, COP28 has set a new course for the international community.
Moreover, the conference marked an important moment in the global conversation about energy storage. COP28 emphasised the potential of energy storage to significantly shape a sustainable energy future. Initiatives such as the Supercharging Battery Storage Initiative, BESS Consortium, and Net Zero World all point in one direction, addressing energy poverty, promoting sustainability, and achieving clean energy goals. To achieve this, we need all battery chemistries.
The conference's outcomes indicate a renewed commitment to accelerating the development and deployment of these technologies. As energy storage becomes more widespread and cost-effective, it will play a critical role in addressing climate change, ensuring energy access, and creating a more resilient and sustainable energy system.
The Consortium for Battery Innovation is actively involved in the rollout of advanced lead battery energy storage systems to contribute to global climate goals. In two ongoing energy storage projects, LoCEL-H2 and Aftrak, we are helping develop BESS combined with solar microgrids to provide a sustainable, reliable, low-cost energy system for remote communities. These projects also demonstrate how energy storage solutions are key to achieving a just transition, helping to increase food access, health outcomes and gender equality. With more energy storage projects underway, CBI will continue to support sustainable development for a climate-resilient future.
The Consortium for Battery Innovation's impactful presence at European Commission’s SET Plans Conference
In the ever-evolving landscape of energy storage, the Consortium for Battery Innovation (CBI) stands at the forefront, driving advancements in battery technology. At the recent SET Plans Conference in Viladecans, the CBI had a strong presence with its Senior External Affairs Manager, Nicola Filizola, showcasing the consortium's commitment to fostering collaboration and innovation within the energy transition landscape.

The revamped SET Plans to address energy policy
The European Strategic Energy Technology (SET) Plan was established in 2007 and since the creation of the energy union in 2015, it became one of the main instruments of the energy union’s 5th pillar on research, innovation, and competitiveness.
During the conference, the European Commission confirmed its commitment to reinforcing the SET Plan, and its acknowledgement of the key role that the initiative will play in delivering the European Green Deal, REPowerEU and the Green Deal Industrial Plan, with a particular emphasis on the Net Zero Industry Act. This will help to accelerate the clean energy transition, increase the EU’s competitiveness, and ultimately deliver the EU’s ambitious climate and energy objectives.
Boosting European competitiveness and technology sovereignty
The EU is a frontrunner in the deployment of sustainable energy solutions and in clean energy research and innovation. However, this leadership is not matched by an equally strong position in the manufacturing of net-zero technologies.
To strengthen Europe’s technological and industrial sovereignty, the European Commission has proposed the Green Deal Industrial Plan, which includes the Net-Zero Industry Act for increasing the EU manufacturing capacity of net-zero technologies, and the Critical Raw Materials Act for securing the supply of critical raw materials. The revised SET Plan will help convert innovations into marketable solutions that can be produced and scaled up in the EU.

Advancing battery technologies
The SET Plans Conference served as a global platform for discussing Sustainable Energy Technology Plans, bringing together experts, policymakers, and industry leaders to deliberate on the future of energy technologies. The CBI consortium's presence was crucial in highlighting the pivotal role that advanced lead battery technologies play in achieving sustainable energy goals.
As the battery industry continues to play a pivotal role in the global transition to clean energy, the CBI's active participation in conferences of this nature reinforces its position as a driving force in shaping the future of energy storage.
For more information on how to develop and reinforce the Brussels footprint for the advanced lead battery ecosystem, feel free to contact our Senior External Affairs Manager at nicolafilizola@batteryinnovation.org
Europe's commitment to renewable energy in the face of climate change
Climate change is happening right before our eyes and presenting new challenges for the world. European communities are grappling with increasingly frequent and intense extreme weather events that have profound impacts and demand our attention. The consequences are severe, from urban areas transformed into fiery landscapes during sweltering heat to towns inundated by floods.
The root cause of the climate crisis is our heavy reliance on fossil fuels. Burning these fuels releases greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, trapping heat and warming the planet. This disturbs the delicate balance of our climate system and intensifies the occurrence of extreme weather events. To face this crisis, we need to move towards a cleaner future with renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power. In addition to reducing our dependence on fossil fuels, renewable energy is essential for strengthening community resilience. This aligns with the European Union’s Green Deal, which outlines a comprehensive set of policies aimed to achieve a carbon-neutral economy by 2050.
European summer of extremes
This summer, Europe experienced a series of record heatwaves and devastating wildfires that have swept across the continent. The European Forest Fire Information System reports that up to 41% of the area burned in the EU is in Natura 2000 protected sites. In 2023 alone, wildfires have released more than 20 million tonnes of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, exceeding the European average over the last two decades.
The Mediterranean region was hit hardest by this year's heat waves. The streets in Greece's ancient port town of Gytheio shimmered as temperatures climbed to an astonishing 46.4 degrees Celsius, setting a new record since record-keeping began in 2006. Life stood still in the sweltering heat, and the streets remained deserted. The heatwave also triggered a wave of wildfires that ravaged the countryside. Nearly 20,000 tourists abandoned Rhodes hotels due to the threat of wildfires, marking the largest evacuation of its kind in the country's history. The intensity of the heatwave caused widespread power outages and plunged towns into darkness. Hospitals struggled to maintain patient care, and businesses were forced to shut their doors.
In May 2023, Italy found itself in the grip of unforgiving weather. The tranquil rivers of Tuscany turned into raging torrents that surged through towns and villages, leaving destruction in their wake. Homes vanished beneath the rising waters, and critical infrastructure crumbled under the weight of the deluge. The downpours lasted 80 hours of relentless rainfall over six days, causing flooding and infrastructure collapse, leaving the affected areas in darkness. Over 20,000 citizens were forced to evacuate and seek refuge in temporary shelters such as schools, sports halls, and gyms.
Not only floods but also severe storms with strong winds are becoming a pressing concern in Europe. This year, Norway faced several relentless storms marked by a historic amount of rainfall. The Norwegian meteorological institute reported extremely heavy rainfall in parts of Norway, marking the strongest in the last 25 years. As winds and heavy rain swept across the region, trees were uprooted, flights faced delays, ferries stopped running, and power lines scummed to disruption. In cities like Oslo, people were urged to work from home. Meanwhile, in the small village of Bagn, nested in the heart of a valley surrounded by forests, landslides wreaked havoc, severing its residents from the outside world.
Researchers at Newcastle University predict extreme weather events will become more frequent due to the climate crisis. "Alongside drastically cutting emissions, countries must build more resilient infrastructure," the researchers said.

Renewable energy and climate resilience
In the face of a changing climate, Europe is at a crossroads. Floods, wildfires, and storms dominate the headlines. As extreme weather events become more frequent, the transition to renewable energy is necessary. The European Union recognises this need and has adopted bold initiatives such as the European Green Deal, a comprehensive roadmap to reach climate neutrality by 2050. Central to this strategy is the Fit for 55 initiative, which aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by at least 55% by 2030. Additionally, the RePower EU plan aims to decrease the dependency of the European Union on Russian fossil fuels and promote green energy.
These initiatives address the challenges highlighted by the extreme weather events. By transitioning to renewable energy, Europe reduces its dependence on fossil fuels and mitigates the effects of climate change. Renewable energy, coupled with energy storage systems, can enhance communities' resilience and help them withstand increasingly severe weather events. Renewable energy ensures a reliable electricity supply amid widespread damage from floods, provides backup power to fire stations during wildfires, and restores power to villages cut off during severe storms. As Europe navigates through new climate challenges, transitioning to clean energy becomes a vital tool to help us ensure a safer and more sustainable future in the face of these extreme weather events.
Want to know more about CBI’s work to achieve a carbon neutral economy in Europe? Subscribe to our newsletter here.
Low-cost, Circular, plug & play, Off-grid Energy for remote Locations including Hydrogen
Funding: Horizon Europe
Duration: 1 January 2023 – 31 December 2026
Project partners: Consortium for Battery Innovation, Commissariat a l'Energie Atomique et aux Energies Alternatives, Hollingsworth & Vose, HOPPECKE Batteries, Lahore University of Management Sciences, Loughborough University, RHYDE, Sunkofa Energy, Università degli Studi di Napoli Federico II, University of Gabes
LoCEL-H2 (Low-cost, Circular, plug & play, Off-grid Energy for remote Locations including Hydrogen) is developing a new solution to bring renewable electricity and clean cooking fuel for off-grid communities.

The solution comprises three core technical innovations:
LoCEL-H2 will conduct two pilot programs, one located in Zambia and the other in Côte d’Ivoire, assessing each community’s energy needs and tailoring the solution in order to provide renewable energy and cooking fuel for approximately 30 households and businesses in each pilot.
For more information visit project's website: https://locelh2.org/

Europe’s bold plan for clean air and economic growth
Climate change is unfolding right before our eyes. While discussions surrounding it have persisted for decades, the time for mere discourse has passed. This year, we saw Arctic sea ice hit record lows during winter, endangering polar wildlife and accelerating global warming. In contrast to the ice decline, Europe experienced devastating floods in many countries. Heavy rains and high river levels caused widespread flooding, affecting communities and infrastructure. These are not isolated incidents but signs that our planet is in distress. It is now crucial to translate words into action. That's precisely where the European Commission’s Fit for 55 package takes the stage. As a vital part of the EU's Green Deal, this visionary plan is strategically crafted to tackle the pressing challenges of climate change. Its main objective is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in the European Union by at least 55% by 2030. As the world heats up and our environment gets sadly more unpredictable, Fit for 55 steers towards a greener, more sustainable future.
At the heart of this change is energy storage. In the context of the Fit for 55 package, there are several reasons highlighting its importance. Energy storage fuels the transition to environmentally friendly transportation and green mobility. This is possible through innovations like smart grids and battery systems powering electric buses in urban areas. Such integration of energy storage with public transportation not only reduces emissions but also makes green mobility accessible. Energy storage opens up job opportunities and boosts local communities. Furthermore, it is crucial in making energy more affordable, offering a safety net for those grappling with rising energy costs.
Driving the energy transition
As a result of the Fit for 55 initiative, energy storage operates on three essential fronts: improving air quality, generating job opportunities, and stabilising energy prices.
Air pollution is a serious problem affecting millions of people around the world. It can cause respiratory problems, heart disease, and cancer. Improving air quality is one of the key goals of the Fit for 55 package. It sets a bold target: zero emissions from new cars and vans by 2035. Energy storage is a vital driver in this journey to reduced air pollution and eco-friendly mobility.

Electric cars are the ambassadors of emission-free transport, and energy storage has the ability to power them. Energy storage also provides backup power for charging stations, ensuring that electric car owners can always find a place to recharge. Electric cars produce fewer emissions than traditional diesel-powered cars, and increasing their use helps to improve air quality. It is a stride towards a future defined by greener travel, with less smog and more fresh, clean air.
Cities and towns all over Europe are tapping into the potential of energy storage, harnessing electricity from renewable sources like the sun and wind. This stored energy fuels the urban transit networks, providing a lifeline to buses and trams. The result? A sharp decline in air pollution, quieter streets, and reduced reliance on fossil fuels. Energy storage acts as a safety net for electric buses and trains, improving the resilience and reliability of public transportation systems. In the event of a power outage, energy storage can provide backup power, ensuring that the city's transport continues to operate. Energy storage becomes an indispensable sidekick as the world shifts towards green transportation, creating a healthier environment.
Added to the industrial new development, there is another aspect of European’s stagnating and lasting issue: high employment rates. The job market is evolving unprecedentedly, leaving job seekers and employers grappling with new challenges and opportunities. As the global appetite for renewable energy grows, so does the demand for a diverse and skilled workforce. The Fit for 55 package aims to create more job opportunities within the clean energy sector. Energy storage, among other clean energy solutions, calls for an array of professionals, from engineers and technicians to electricians and software developers.
When an energy storage company establishes a new factory in a rural area, it does not only bring job opportunities to the community but also stimulates the local economy. The ripple effect is significant, as various services are required to support the factory. Construction workers, transportation services, and material suppliers all benefit from the newfound wave of activity. This synergy, driven in no small part by energy storage, highlights the potential of clean energy to power our homes, livelihoods, and economies.
Affordable energy is a pressing concern for communities and individuals globally. The COVID-19 pandemic and the war in Ukraine have aggravated the energy crisis, pushing energy prices to record highs. This is having a devastating impact on people and businesses, particularly those who are already struggling to make ends meet. The Fit for 55 package seeks to make energy more wallet-friendly for everyone, and energy storage is central to this vision.
Energy storage allows storing electricity during quiet hours when it's less expensive and tapping into these reserves when electricity prices skyrocket during peak demand. It's akin to purchasing energy at a discount rate and seeing savings grow.
Energy storage fosters self-reliance, particularly in regions prone to power hiccups or environmental concerns. Community solar initiatives, often supported by energy storage, are expanding access to solar energy, cutting the cords to the traditional power grid. This approach delivers a double victory, benefiting our finances and the planet's well-being.
Integrating an energy storage system for homeowners with solar panels complies with having a personal vault for energy. During the day, the excess energy is safely stored away. This energy is later used to lighten homes without sending electricity bills soaring. Energy storage systems are transforming the energy landscape, addressing the energy affordability crisis and making it more accessible for everyone.

Towards a greener future
While the Fit for 55 package may initially seem like a distant, abstract concept, its impact is already spreading through our daily lives. Together with energy storage, this visionary strategy has the potential to redefine our homes, our cities, and our communities. Energy storage fuels the shift to environmentally friendly transportation, cleansing the streets and reducing our dependence on fossil fuels. Energy storage solutions create job opportunities, uplift local communities, and place affordable energy within reach.
When the Fit for 55 package and energy storage team up, they have the potential to transform societies, reshape our relationship with the environment, and pave the way for a greener, more sustainable world.
Uncovering the key role of energy storage in Europe's green revolution
In the scorching summer of 2023, Europe was gripping an unprecedented heatwave. This extreme weather triggered a series of devastating events, including wildfires raging through Southern France and droughts that left the water reservoirs in Spain critically low. Such disasters were a stark reminder of the pressing need to address climate change head-on, an undeniable call to action.
In response, the European Commission and the cities across the continent have united, propelling Europe toward a more environmentally conscious future. At the core of this collective effort lies the Effort Sharing Regulation, which assigns emission reduction targets to each member state. With their sights firmly set on these targets and a dedicated commitment to combat emissions, European cities are charting a course towards sustainability, driven by innovation and a shared vision of a greener tomorrow.
This article explores three local initiatives - Copenhagen’s and Barcelona’s Climate plans and Tallinn as Europe’s Green Capital. Together, they exemplify how cities actively invest in renewable energy, advocate for sustainable transportation, and advance emission reduction. What unites these cities is their reliance on energy storage, with batteries emerging as integral components within these systems.
A green wave all over Europe
In the heart of Catalonia, Barcelona takes a bold stance in Europe’s ongoing battle against climate change. The city’s Climate plan sets a clear course towards reducing emissions and embracing renewable energy. At the forefront of this environmental mission are energy storage systems, with time-tested batteries powering businesses and homes across the city.
Barcelona’s first energy community epitomises this shift. Along the bustling Barcelona Port, solar panels soak in radiant Mediterranean sun. What sets this community apart is its ability to capture excess solar energy, preventing it from going to waste. Instead, it’s harnessed by energy storage systems. This stored energy becomes a precious resource, fueling essential port operations, from lighting to refrigeration. The Barcelona Port stands as an exemplary testament to the transformative potential of energy storage, pushing the city toward its climate goals one watt at a time.

Copenhagen has set an ambitious goal: to become the world’s first carbon-neutral capital by 2050, as outlined in its Climate plan. This visionary concept encompasses many initiatives, all connected by a central theme, energy storage.
A standout feature of the plan is Copenhagen’s extensive electric bus fleet, powered by battery energy storage systems. These systems store the energy that propels emission-free buses along the city’s bustling streets. In 2021, Copenhagen made waves by introducing 100 electric buses, to reduce annual greenhouse emissions by 5,000 tons. The city’s vision stretches even further, anticipating 50,000 electric vehicles on its roads by 2025, with advanced energy storage technologies seamlessly integrating modernity into urban life.
Copenhagen’s Climate plan encompasses initiatives ranging from retrofitting buildings with energy-efficient technologies to harnessing wind turbines and photovoltaic systems. In this vibrant metropolis, we witness the potential that arises from the marriage of renewable energy and energy storage solutions.
One of Europe's greenest cities is Tallinn. This progressive city with mediaeval charm was honoured with the European Green Capital 2023 title, recognising its ambitious sustainability plans. To achieve carbon neutrality, Tallinn is making substantial investments in renewable energy and energy-efficient initiatives. The city’s strategic approach to sustainability hinges on energy storage and the development of a smart grid, using digital technology to manage the flow of electricity.
A shining example of Tallinn’s commitment to energy storage is Ülemiste City Energy Storage Park. A robust energy storage system is nested within the park, ensuring no clean energy goes to waste. The park reduces the city's dependence on polluting fossil fuels and paves the way for increased local clean energy generation.
Tallinn’s mayor, Mihhail Kõlvart, firmly believes cities will be crucial in achieving European climate and sustainability targets. “European Green Capitals need to take leadership in creating sustainable, resilient and inclusive cities of the future to ensure a high-quality living environment,” stated Kõlvart, emphasising the value of collaboration among cities.

A sustainable energy storage transition
These local initiatives showcase the proactive spirit of European cities in the battle against climate change. In their stories, energy storage is a bridge connecting renewable energy to our daily lives. In Copenhagen, energy storage ensures swift and modern public transportation. In Tallinn, it fuels the city’s green revolution. In Barcelona, it keeps the bustling port community in motion.
With their progressive climate plans, these cities remind us of the importance of energy storage and its role in achieving the goals set by the Effort Sharing Regulation and the European Green Deal. By hopping on the energy storage bandwagon, cities across Europe are speeding toward a sustainable and low-carbon future.
New Report Reveals How Lead Batteries are Featured in Chinese Energy Storage Systems
As the global power industry wrestles with the need to expand energy storage to accommodate renewable generation and meet soaring demand for electricity overall, a new CHR Metals Limited report states that countries like China are shifting some focus toward lead batteries over lithium for battery energy storage systems.
“The growth of lead battery energy storage systems in Asia, especially in China, is promising, driven by efforts to reduce fossil fuel use and achieve net-zero goals,” said Dr. Alistair Davidson, director of the Consortium for Battery Innovation. “With the energy storage market expected to exceed 400 GW by 2030, the CHR Metals analysis highlights significant opportunities for lead battery projects regionally and globally.”
Currently, only lithium-ion and lead batteries operate on a scale sufficient to meet demand, representing over 98 percent of the rechargeable battery market through 2030.
Lead batteries, known for their efficiency and reliability, continue to play a vital role in backup power for critical infrastructure, hybrid automotive, and motive power applications. Advanced lead batteries emerge as an ideal solution for energy storage, boasting superior performance, safety, and scalability to align with the U.S. and E.U.'s net-zero emission goals for 2050.
This week’s CHR Metals Limited Report also notes:



Contrary to misconceptions, lead batteries stand out as the most recycled and innovative products globally, minimizing the carbon footprint by utilizing recycled materials. Over 97 percent of lead batteries in North America and Europe are collected and recycled, with 85 percent of the recycled lead used in manufacturing new batteries—a testament to the circular economy in action. (Source: Association of Battery Recyclers)
Lead batteries can help deliver on climate-neutral pledges and provide energy resiliency in specific applications.
“Despite ongoing misconceptions, ongoing research and innovation have propelled advanced lead batteries to impressive strides in performance over the past decade,” added Davidson. “These advancements, including improved cycle life, lifetime, and overall energy efficiency, translate into substantial benefits in terms of total cost of ownership and reliability.”
While embracing an overall diversification of energy sources and plans to increase renewables, the versatility and proven performance of advanced lead batteries position them as a scalable and cost-effective solution to meet today's demands and future energy storage needs.
September 26, 2023
By Alyssa McQuilling
The Electric Power Research Institute’s (EPRI) Energy Storage Integration Council (ESIC) held a Strategy Meeting on September 14, 2023 at the JW Marriott in Indianapolis to focus on identifying the energy storage gaps and how ESIC can address them.
The mission of ESIC is to advance the deployment and integration of energy storage systems through open, technical collaboration.
This meeting was open to the technical community of energy storage stakeholders, such as electric utilities, energy storage developers and integrators, regulators, system operators, independent power producers, and research and consulting organizations.
As the technical voice of the lead battery industry, CBI sent US Research and Innovation Manager, Dr. Alyssa McQuilling, to share and collaborate on industry insights.
Her takeaways from the event included:
Lastly, the six national labs have to a role to play in getting emerging technologies ‘over the hump’ in terms of development. This includes those opportunities created through Grid Storage Launchpad and ROVI (Rapid Operational Validation Initiative).
We look forward to seeing CBI’s members transform projects into products that can benefit industry and utilities in meeting their renewable integration and decarbonization goals.



The European Energy Transition
By Nicola Filizola
As the world copes with the urgent need to address climate change and reduce greenhouse gas emissions, Europe has been leading the charge in transitioning to a cleaner and more sustainable energy future. The European energy transition is a comprehensive shift from traditional fossil fuels to renewable energy sources, such as wind, solar, hydro, and geothermal power. Among the critical components enabling this transformation, lead batteries have emerged as a key technology that plays a pivotal role in the transition's success. In this article, we will explore the energy transition in Europe and delve into the essential role that batteries are playing in shaping the continent's greener and brighter future.
The Growth of Renewable Energy in Europe
The European Union (EU) has been at the forefront of advocating for clean energy and sustainability. Through initiatives like the European Green Deal and the Paris Agreement, EU member states are committed to reducing their carbon emissions, fostering innovation in clean technologies, and achieving climate neutrality by 2050.
One of the main challenges of integrating renewable energy sources into the existing energy infrastructure is their intermittency. Solar and wind power, for instance, depend on weather conditions and daylight availability. To ensure a stable and reliable energy supply, an efficient energy storage system is essential, and that's where batteries come into the picture.
The Challenge of Intermittency
Unlike conventional power plants that can provide a consistent energy output, solar and wind power are dependent on weather conditions and natural variations. Cloudy days and calm winds can lead to a drop in power generation, causing fluctuations in the grid. This intermittency poses challenges to grid stability, and the power supply must be balanced in real-time to meet demand. If renewable energy sources are to dominate the energy mix, an effective and efficient energy storage solution is imperative to address this variability.
Batteries: The Key to Storing Renewable Energy
Batteries are essential components of the energy transition as they serve as a bridge between renewable energy generation and consumption. These energy storage systems can store surplus electricity when generation exceeds demand and release it when demand surpasses generation. In essence, batteries help to smooth out the intermittent nature of renewables and provide a stable supply of electricity to the grid.
Batteries act as buffers, absorbing excess energy during periods of high generation and releasing it when generation dips. By doing so, they stabilize the grid and ensure a steady supply of electricity, reducing the risk of blackouts and power disturbances. Moreover, batteries can respond rapidly to fluctuations in demand, providing grid operators with a valuable tool to manage the grid effectively.
The energy transition in Europe is also characterized by a shift towards decentralization, with an increasing number of small-scale renewable energy installations, such as rooftop solar panels and community wind farms. Batteries play a vital role in this decentralized energy landscape by enabling consumers to store and manage their locally generated energy. This promotes energy autonomy, reducing the reliance on centralized power plants and enhancing energy security.
Batteries make it possible to integrate a higher share of renewables into the grid. By storing excess energy during periods of high generation, batteries ensure that the energy is not wasted and can be used during times of low generation. This feature is particularly crucial during seasonal variations when renewable output may vary significantly.
Batteries also play a significant role in electrifying transportation, another essential aspect of the energy transition. The growth of electric vehicles (EVs) is dependent on advanced battery technology, allowing for longer driving ranges and faster charging times. Widespread EV adoption not only reduces greenhouse gas emissions from the transportation sector but also opens up the possibility of using EV batteries for grid storage through vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology.
In conclusion
The energy transition in Europe represents a monumental effort to combat climate change and create a sustainable energy future. The integration of renewable energy sources is a crucial step in this journey, but their intermittent nature presents challenges that must be addressed. Lead batteries, together with other technologies, emerge as the silent protagonists, providing a robust and reliable energy storage solution. From enhancing grid stability and enabling renewable integration to empowering decentralized energy systems and fostering electric vehicle adoption, lead batteries will play a multifaceted role in reshaping Europe's energy landscape. As technology advances and costs continue to decline, the potential of batteries will only grow, propelling Europe towards a cleaner, greener, and more resilient energy future.
The lead battery industry could be in line for a $10 billion share of the burgeoning energy storage market within the next decade.

Research into upcoming projects and opportunities indicated that the ESS landscape is forecast to be 550GWh by 2030 with a value of $30-$50 billion for all battery technologies.
The lead battery industry has set its sights on securing 100GWh of that potentially lucrative ESS market.

CBI launched its first technical roadmap in 2019 setting specific goals for the end of 2022.
“It was all really market-driven. We used those targets to select our program. And the result of the
projects that we funded have pretty much shown that we delivered on these goals that we set.”
There are now batteries on the market, primarily from our members in the US and Asia, that meet that criteria.
This means there are now have advanced lead batteries on the market-oriented toward ESS that have an impressive globalized cost of ownership for the system, says Raiford.
“The way we view it as battery scientists is cycle life — most key stakeholders look at it from total cost of ownership.
“So we see stationary batteries now that really perform along the lines of lithium.”
Read the full article from Batteries International
22nd September 2023

The 7th World Energy Storage Day (WESD) Global Conference & Virtual Expo, 22nd September 2023 and is a virtual, 24-hour marathon conference covering 100+ countries including topics like Energy Storage Manufacturing, Innovation, Supply Chain, Mechanical Storage, Thermal Storage, Electro-Chemical Batteries, Energy Access, Stationary Energy Storage, Energy Storage Financing, Investment, ESS, EV infrastructure, Battery Swapping, Urban Air Mobility (UAM), EV OEMs, Battery Recycling, Circular Economy, Global Start-up showcase, Start-up workshop, Women in Energy and Green Hydrogen applications & Manufacturing.
The WESD platform is one of the largest open (Free to attend live) global events in this domain. The event is supported by Gold Partner UL and supporting Partner Green Hydrogen Organisation (GH2), MENA Energy Storage Alliance (MENA-ESA), Thailand Energy Storage Association (TESTA), Consortium of Battery Innovation (CBI), Eurobat, Smart Energy Council (SEC), Innovation Norway, Scotland Development International, LDES Council, Batteries European Partnership Association (BEPA), Global Renewables Alliance and others.

The Consortium for Battery Innovation connected with over 730 attendees from 42 different countries representing 319 different organizations in Siem Reap, Cambodia for the 20th Asian Battery Conference (20ABC) and the Recycle 100 International Secondary Lead Conference and Exhibition that featured global discussions on the world of lead, recycling, lead-acid batteries and energy storage.
CBI Senior Technical Manager, Dr. Matt Raiford said that lead batteries are made and produced in over 100 countries, and the Asian Battery Conference was a great venue to see how Asia, Africa, and other areas of the world are innovating and improving lead battery technology. For instance, CBI member companies, Hammond and Borregard, demonstrated deeper understandings of additive chemistry as a low threshold method to improve lead batteries for many different applications.
CBI participated in the line-up of over 45+ conference speakers during 20ABC to share our technical battery knowledge and insights with attendees with presentations that included:


The 20th Asian Battery Conference provided a chance to join several technical sessions providing valuable insights from industry leaders, market analysts and technical experts about the lead battery industry. Several speakers including CBI member companies presented innovations and advancements, such as new active material formulations and improvements in the manufacturing process, for several applications of lead batteries.
Dr. Begüm Bozkaya, CBI’s Technical Manager, shared that there are definitely future opportunities for lead battery technology in Asia and other continents of the world via the implementation of new developments to deliver cost-efficient, safe, and sustainable battery solutions.


8th International Secondary Lead & Battery Recycling Conference covered several aspects of lead recycling industry in Asia and Africa. Bozkaya shared that many of the speakers addressed the current issues related to environmental challenges, financial, and social risks in the secondary lead industry. It was beneficial for attendees as some of the ILA & CBI members also illustrated their new techniques and developments in recycling of lead batteries.
Recycle 100 illustrated the ins and outs of running battery recycling centers - the heart of lead battery sustainability. Raiford was intrigued by ongoing improvements at Asian recycling operations, especially in increasing recycling efficiency - and how these improvements were presented to representatives from dozens of countries.
The city of Siem Reap, Cambodia was an amazing host and we enjoyed seeing all the beautiful areas in that region. The 20ABC was a successful event from all angles – including the achievement from the event’s charity initiative. The "ONE Minute Giveback", exceeded organizer’s and sponsor Sorfin Yoshimura’s expectations, by raising over $22,000.00 USD to help fund a bed in the Oncology Department of Angkor Hospital for Children.







We look forward to next year’s events and continuing the technical conversations around lead batteries.
The Department of Energy (DOE) held its Energy Storage Grand Challenge Summit (ESGC) online and in Atlanta, GA on July 25-27, 2023.

Dr. Alyssa McQuilling, CBI’s U.S. Research and Innovation Manager, shared her thoughts and key takeaways from the event.
McQuilling noted that this is an unprecedented time for the development of energy storage with historic investments being made by the federal government to aid in commercialization.
As the DOE and other agencies are taking an “all of the above" approach to meeting the demands of a modern grid; there’s room for all the technologies to meet customers’ needs for a reliable grid (while also maintaining affordability).
At CBI, we encourage participation from all technologies to meet the growing global energy storage demand. CBI organized a response from the U.S. industry, and DOE ESGC efforts used the feedback from CBI members in a DOE Lead Battery Lift-off Report.
In this report, an in-depth analysis of lead battery innovation pathways was conducted, resulting in portfolios of lead battery improvements capable of helping the DOE reach the 0.05$/kWh/energy throughput goal outlined in the ESGC. These improvements include advanced manufacturing, improving cycle life, advanced control algorithms, standardization of devices and protocols, and demonstration projects to understand the impact of scaling on cost.
At the same time, we recognize how well-suited lead batteries are because they are a cost-effective, safe, and reliable solution. DOE recognizes lead batteries for this value as part of the energy storage solution as they currently represent much of the market.
Another takeaway is the ongoing emphasis on U.S. manufacturing, jobs, and ensuring that historically underserved communities also benefit through adopting energy storage technologies.
As a result, it will become increasingly important to make new connections that can accelerate growth in the industry because (again) the speed at which things are developing is unprecedented. These connections are critical and include collaboration and working across industries.
In the last session of the summit, the discussion focused on ROVI, or Rapid Operational Validation Initiative, (part of a collaborative effort from 6 national labs) to figure out how to model system performance/degradation/failure for different battery technologies by combining approximately one year of system data with machine learning/AI modeling approaches to figure out how the system will perform over a 15 to 20 year lifetime.
CBI is answering the many DOE opportunities by utilizing the breadth and expertise of our membership and bringing in key institutions and systems providers. These collaborative teams are poised to deliver a high-performing, sustainable, domestic solution to meet the many goals of the ESGC.
Below are two Energy Storage Innovation reports that were recently released:
Planning is Underway for LoCEL-H2, a Four-Year, €10million Sustainable Energy Storage Project, Co-funded by the European Union
[LE BOURGET-DU-LAC, February, 2023] – A recently won European Union project by the Consortium for Battery Innovation (CBI) will pair advanced lead batteries with green hydrogen to deliver a new source of clean, reliable, and sustainable energy storage for off-grid communities in Africa.Awarded through Horizon Europe, this collaborative, four-year project called LoCEL-H2, (or Low-cost, Circular, plug & play, Off-grid Energy for remote Locations including Hydrogen), combines the expertise of lead battery manufacturers, academia, national laboratories, component manufacturers, and companies who are focused on integration, microgrids and renewables.
LoCEL-H2 will generate renewable energy, storage, and fuel for deployment in isolated and remote regions of Africa, to support communities that cannot connect to an electricity grid.
“The excitement around this innovative project is reflected by everyone involved,” said Dr. Carl Telford, the senior research and innovation manager at CBI. “Energy poverty is a problem that affects millions of people worldwide because they lack consistent access to electricity.”
The majority of the world’s population living in energy poverty are in Sub-Saharan Africa and are dependent on traditional stoves and fuels for their cooking. As a result, most of the domestic chores are handled by the women in these households, who then develop an increased health risk from a constant exposure to biomass, kerosene and/or coal fuels used for cooking.

The LoCEL-H2 project will provide a sustainable energy source as well as access to clean fuels. Another benefit will result in the education levels within these communities being positively impacted since they will now have access to online information through a reliable energy connection.
“This project is important to help address the United Nations Sustainable Development Goal 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy), while having an impact on other areas such as health,” noted Dani Strictland, professor of electrical power engineering at Loughborough University and a member of the LoCEL-H2 partnership.
This project involves nine partner companies across western Europe who will develop new technology for a novel distributed microgrid, as well as a Battolyser. The Battolyser is a new solution for producing clean hydrogen technology to power cooking surfaces and would replace biomass fueled stoves.
Whether as a response to climate impacts or future energy storage needs, advanced lead batteries are often an overlooked and innovative technology that bring safe, reliable, low-cost solutions to pair with a renewable source.
By combining lead batteries with wind and solar power, this forward-looking energy storage project will deliver ongoing, affordable electricity to off-grid communities and become a deployable solution for other energy-deprived areas around the globe.
The two pilot areas for the project will be focused in Zambia and Ivory Coast. Angel Kirchev, a senior expert, Ph.D., HDR, at CEA Tech and LoCEL-H2’s project coordinator said, “CEA looks forward to coordinating this exciting and challenging 4-year project which will bring sustainable energy and green hydrogen to challenged communities.”
Watch our LoCEL-H2 Kick-Off Video here.
![]() Project Co-Funded by the European Union
Project Co-Funded by the European Union
The members of the partnership are CEA, Hoppecke, Hollingsworth & Vose, UNINA, Loughborough University, Sunkofa, University of Gabes, SAS Réseaux Hydrogène Décarboné RHYDE, and LUMS.
Contact: Lara Wilson
CBI Sr. Communications Manager
Lara.wilson@batteryinnovation.org
About Consortium for Battery Innovation
The Consortium for Battery Innovation (CBI) is the world’s only global pre-competitive research organization funding research into lead batteries for energy storage, motive, and automotive applications. For more than 25 years, with its global membership of battery manufacturers, industry suppliers, research institutes, and universities, CBI has delivered cutting-edge research pushing the boundaries of innovation in lead battery technology, setting the standard for advanced lead batteries and the next generation of energy storage.
For more information, visit our website: batteryinnovation.org
About Loughborough University
Loughborough University is the home of world leading engineering, with an international reputation for being at the forefront of technological innovation and for maintaining extensive links with industry. The Wolfson School of Mechanical, Electrical and Manufacturing Engineering is one of the biggest engineering schools of its kind in the UK. The school aims to provide international leadership in research and innovation with a focus on climate change and net zero and has an unrivalled educational experience. Loughborough University is consistently in the top 10 in many university ranking tables for student experience.
Learn more at lboro.ac.uk/departments/meme/.
###
They are the future of the lead battery industry: highly-educated, motivated and brimming with new ideas and ambition. CBI spoke to three talented scientists, new to the lead battery industry, to find out more about their perceptions of the workplace and to hear their suggestions about how the industry can continue to attract the brightest and the best.
Max Parker, a PhD Student at Warwick University (United Kingdom); Miguel Rodríguez Gómez, PhD Student at INMA (Spain) and Grace Rocha, a Scientist at ITEMM (Brazil). From industry’s first impressions, learning new areas for innovation and crucial for our future, to the industry’s urgent effort to attract more young talents, they are the voices of a new generation inside the lead battery industry and here’s how they feel about it.

CBI : Tell us a bit about when you first joined this industry. What were your expectations ?
Max : « Batteries are an exciting area with a lot of areas to look at and lots of different things to analyse. Before joining the industry I didn’t really know what made one battery better than the next, why this one can charge faster than the other or why this one lasts longer than the other. Lead batteries are interesting because they have been around for such a long time, but there is still so much more to look at, and still so much more to learn. »
Grace : « To be really honest I didn’t think very much about the whole Lead Battery industry. I just wanted to be part of a great industry with a great social impact, which everybody near around knows Moura does to the city and to the state. Now, I am truly surprised with how much I enjoy working on the field. I see that there is a excitingopportunity for progress learning and development in every area of lead battery technology. »
Miguel : « I had just finished my masters degree and I was looking for research into something related to the energy or climate crisis. Energy storage is essential to be able to cover the off-peak hours of renewable production, and to move away from fossil fuels (which also have rapidly diminishing reserves). So, I started to look for research lines related to batteries. The truth is that I knew almost nothing about lead batteries, I thought there were only in cars and little else, but when I learned a little more and discovered that they can be used for many things and above all that recycling is very high, I decided to go for it.”

CBI : And now that you’ve been working for the industry, what’s your current perception ?
Max : « I think that there are lots of challenges ahead for the world of lead batteries. I would like to see more innovation to meeting these challenges, especially in the energy storage sector, which will be a big part of the future of lead batteries. Innovation is constant, and constantly necessary, because the use cases of lead batteries are changing. We need to be providing the new and innovative batteries of not just today but also the future. »
Miguel : « There is still much to discover and improve, and I think that since the materials of the batteries are cheap and abundant (but also safe and resistant), it will be very important in the years to come. On the other hand I think that production is too focused on the automotive industry. There is less and less demand for cars worldwide and energy is becoming more and more expensive, so I am convinced that the future is energy storage and back up systems. »
CBI : What can you learn from working with professionals who have been in the industry for a long time? What do you learn from each other in your projects ?
Max : « Professionals with a lot of experience have a wealth of knowledge and, but it is up to them to pass that on. I started from zero knowledge and having an experienced professional to provide guidance would have been of great help to ensure that I wasn’t misunderstanding things. Since being involved with the CBI, it has enabled contact with battery experts within companies and other universities. Some of them can share knowledge that is not as well known or written about in technical literature. And this leads to better experiments, better understanding and better development. »
Grace : « One of my favorite things about my job is the opportunity to network with everybody in the global lead battery chain. I’ve noticed that there is so much contribution on the field. For example, every time I have a call with a supplier, a partner, a specialist, I learn something new. And I feel they are always willing to help, they are so welcoming to answer my questions (and I do have lots of questions !). The Lead battery is not a technology that you learn through on college here in Brazil. So everything I know so far, I’ve learned from their experience. I’m really glad to see how some of the ideas I’ve given actually worked and contributed with the development of the projects. »

CBI : What things would you like to happen in the industry to attract more talent ?
Miguel : « There are two main things to attract younger professionals. The first is to raise awareness of the lead battery industry, communicating its importance globally and showing that it is possible to have a fruitful career in it. The second is to communicate that it is a technology that can help with very important problems that especially (but not only) the younger generations are going to suffer, such as the climate crisis, the energy crisis and the resource crisis. For me personally, it is essential that 99% of the lead in batteries is recycled. I would not like to work with a polluting technology that ends up accumulating in landfills. I also believe that research lines focused on renewable energy storage and batteries for trains (which is the most efficient and less polluting transport, both for people and goods), should be encouraged. »
Max : « From my perspective in the world of academia, I would like to see more PhD funding, more internships, sponsorships and more university partnerships. Early career development and career paths can encourage people to join. Another option would be a summer job/internship/work experience in a battery company. Getting young people into the world of batteries requires investment in them, and guidance. With the right support and guidance a PhD student can produce some excellent research. But without the right funding they will go to do something else, or a PhD in another field. »
Grace : « I believe the answer is undergraduate students. Talking about the Brazil scenario, I would like to see the industry work more with universities. For example, investing in programs to develop new projects for undergraduate students. I think that would be a win/win situation : The students would have the opportunity to work on a real life problem and learn about the lead battery from experts ; and the company would have the opportunity to work with new researchers and a new university department. This is a great way for students to be more prepared before they join a lead battery company.
I think even quick programs like a “Battery Marathon”, something like a Hackathon, would make students curios about the area and starttheir development from college. Today, at ITEMM we are already making this approach. Recently we started the implementation of a research and innovation center in a technical college in the city, focused on developing young talent.»
CBI : Would you recommend the lead battery industry as a place to work for young scientists?
Miguel : « I recommend the lead battery industry to anyone interested in energy storage. It is a well-known technology but there is still a lot of room for improvement, and research is always interesting and fun. From my work I especially like the direct relationship with the industry, which is eager to generate more and more research projects. This year at ELBC, I have learned a lot and it has been a very rewarding experience to learn about the latest advances in research and also to see what the market trends are. »
Grace : « I do recommend. The more I work on the field the more I see there is still so much room for new ideas. It is a great time to be working in the battery field! Environmental care is one of the major concerns around the world, and batteries are key to this! One of the great things about the lead battery industry is that we are a safe technology, critical for energy storage, which helps reduce the global carbon footprint. Something people forget is that we are also an industry that has a true circular economy. »
Both Max and Miguel won this year’s CBI & EUROBAT Student Award, a great way to promote their work in the industry by bringing them to ELBC 2022 as speakers. In 2022, CBI also visited ITEMM in Brazil, where we had the chance to meet Grace and learn about her work at the Research and Development Department.
Interested about their work with CBI? Check out our blogs and videos:
The Global Lead Battery Innovation Conference and Expo (ELBC), co-organised for the first time by CBI, took place in Lyon, France (6-9 Sept).
As a warm-up to the main conference, CBI brought together lead battery industry experts from all over the world, to take part in:
On day one of ELBC, CBI’s Director (Dr Alistair Davison) set out a positive assessment of the opportunities for advanced lead batteries highlighting CBI’s roadmap, which charts a path to a new generation of batteries in a session dedicated to Markets and Trends.
And CBI technical experts, including Begüm Bozkaya, Technical Manager, outlined the CBI technical program with an insightful presentation focusing on improving energy storage systems and automotive batteries as key innovations in the industry.
To promote CBI’s Technical Roadmap and its work in driving innovation across the industry Dr Matthew Raiford, CBI’s Senior Technical Manager updated delegates. And in a major announcement, Dr Carl Telford impressed ELBC attendees with news of a 10 million Euro funding award for an innovative lead-battery powered microgrid project in Africa, brokered by CBI.
In his presentation entitled « Opportunities for Lead Batteries in Energy Storage Systems », Dr Telford spoke about the use of lead batteries for sustainable energy projects and presented for the first time this novel project funded by the European Commission that gathers lead batteries, renewables, and hydrogen.
As always at ELBC there were many networking opportunities, with delegates able to meet face to face for the first time in four years. The well-attended gala dinner took place at La Sucrière, and WGBI’s (Women in the Global Battery Industry) held its first meeting in Europe. This important initiative aims to bring more women to our industry and empower them through networking sessions, workshops, and mentoring opportunities.
CBI is very much looking forward to seeing all these fantastic attendees and delegates again at ELBC 2024 in Milan, Italy.
Watch the Event video: