

A recent Brussels meeting emphasized the need to address the priority for a long-term strategy for Critical Raw Materials in Europe. Following the Ukrainian-Russian conflict, not only war came back to our continent after the end of WW II, but we also witnessed adverse effects, such as soaring inflation, geopolitical tensions, and surging energy costs, significantly impacting our everyday lives. Alongside, with growing consequences of the climate crisis, there is no other action than to transition towards renewable energy sources to lower carbon dioxide emissions and make energy more efficient. In this scenario, the Critical Raw Material Act (CRM) sets out an ambitious vision for Europe that seems to fall short when it comes to financing its promises.
By Nicola Filizola

As I attended the Eurometaux rally on April 18th, discussing Critical Raw Materials, I couldn't help but ponder the complex challenges confronting the global scene today.
The Ukrainian-Russian conflict and its aftermath had unforeseeable consequences.
Inflation, international tensions, embargoes, and a dramatic increase in energy costs have affected every aspect of our lives. Electricity bills have soared, fuel prices have spiked, and industries are facing unexpected cost increases, occasionally leading to business failures.
As this was not enough, in the face of these economic challenges, we are also obliged to confront a harsh reality we’ve long ignored—the climate crisis and its severe implications for our planet and its inhabitants.

Consider this, annually, air pollution from fossil fuels and biomass burning is responsible for 7 million deaths worldwide, with associated costs nearing $30 trillion. By 2050, the financial impact of global warming could reach $25-30 trillion yearly. Shockingly, 90% of this pollution originates from energy sources, highlighting its grave impact on human health and the environment (Jacobson M., 2024, Clean, Renewable Energy & Storage for a Sustainable Future, Stanford University). Our dependence on fossil fuels not only raises pollution levels and keeps energy efficiency low, but also introduces risks of price volatility and geopolitical instability.
There is no way out, humanity stands at a crossroads: take decisive actions to protect our planet and future generations or passively face increasingly catastrophic events.
However, there is hope in this ugly scenario. The power to shape our future is in our hands. Embracing renewable energies such as wind, water, and solar is pivotal to electrifying our homes, industries, and transportation systems. But this shift demands innovation, investment, and political will.
If we are to do that decisively, Europe's green transition is expected to boost the demand for critical raw materials. European companies largely depend on imports for these minerals, with a significant amount coming from China. Therefore, this concentration in supply chains places Europe's climate and green industrial policies at considerable geopolitical risk.
The CRM, a new regulation of the European Commission, is part of the broader Green Industrial Plan and is aligned with the Net-Zero Industry Act (NZIA). It emerges as a vital element in this transition, ensuring the responsible extraction and processing of materials crucial for renewable technologies.
The Act, for instance, aims to diversify supply chains. It has set benchmarks for domestic capacities by 2030: at least 10% of raw materials must be sourced domestically, with targets of 40% for processing and 15% for recycling, reducing dependency on single suppliers.

While the CRM represents a positive and very ambitious step for Europe's strategic autonomy, it doesn’t fully tackle the vastness of the challenge. The Act aims to develop a European supply chain for critical raw materials by simplifying permitting processes, yet it needs to allocate additional funding. There’s no doubt private investment is crucial. However, as demonstrated by the US Inflation Reduction Act ($783 billion in provisions relating to energy security and climate change) mechanisms such as tax credits, grants, and loans can greatly bolster the confidence needed for sustained private investment in decarbonising the industrial sector.
To truly enhance resilience and reduce vulnerabilities, the EU must recognise building such resilience comes with a cost. This implies committing to substantial European funding and administrative support, setting realistic diversification targets for European companies through regulations, and ensuring that necessary resources support external trade and partnership strategies.
We live in an era when smart homes have become part of our everyday lives and energy storage systems are changing the way we think about energy.
Growing up, many of us were captivated by the portrayal of modern and futuristic homes on television. Each depiction was unique, yet they all shared a common charm—a certain "wow" factor that held our gaze, sparking imagination about the endless possibilities technology could bring to the future. Although we may not have parking spots for family spaceships in our backyards just yet, the vision of the future we once admired is closer to reality than we might think.
Today, we live in an era when smart homes have become part of our everyday lives. Our houses now integrate various inventions, all harmoniously working together. By integrating smart technologies that make our homes more energy efficient, we're taking steps towards preserving our planet and addressing the ongoing climate crisis.
Technology meets sustainability
An example of such smart technology is a battery energy storage system. This modern yet increasingly common technology enables us to capture and store energy for later use, marking a shift in how we power our homes. This article takes you on a journey through the modern home, exploring practical and innovative uses of energy storage systems. Transforming what may once have appeared as science fiction into part of the solution for a greener, more sustainable lifestyle, energy storage systems are changing the way we think about energy.
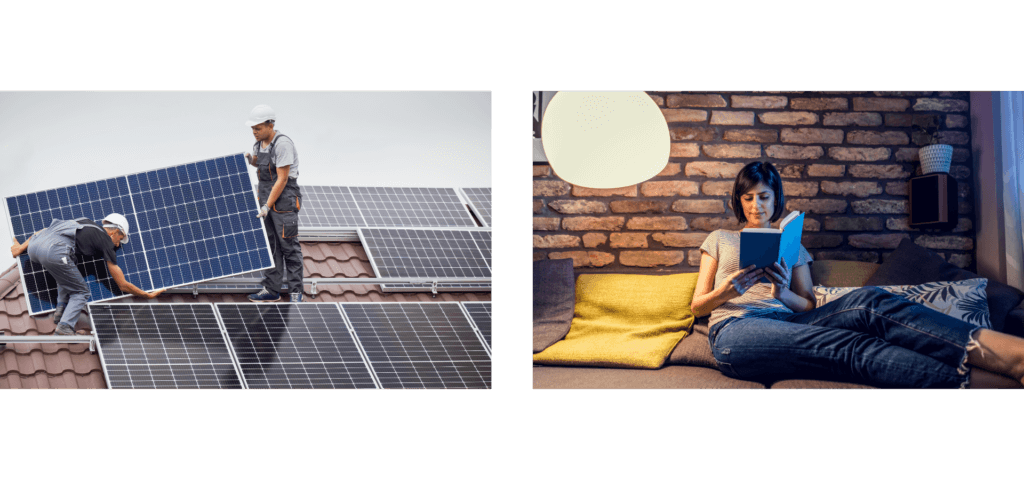

The tour already begins outside the house, where the renewable energy narrative forms under the open sky. Solar panels, discreetly placed on the roof, capture and convert the sun's warmth. This stored energy then finds its way back into the house, supplying hot water for daily use or heating indoor spaces, making every drop of sunlight count. This highlights how sustainability and modern living go hand in hand, showing that even our garden can play a role in powering the home.
As we enter the house and step into the living room, the last rays of daylight fade into the soothing glow of several desk lamps, all backed up by energy stored from today's sunshine. The television, gaming consoles, and even the WiFi router sip electricity from the reservoir of clean energy. This seamless integration of energy storage systems allows us to relax in front of the television after a long day or cosy up on the sofa with a favourite novel under the warm light of the lamp without giving a moment's thought to outside energy constraints.
Smart energy in action
Moving into the kitchen, the narrative of energy efficiency continues. Here, everyday activities continue as usual but with a green twist. Appliances, backed up by an innovative energy storage system, manage power usage with precision. The refrigerator hums quietly to keep the food fresh while the oven preheats for dinner, and the dishwasher stands ready, all running on stored energy. The effortless way the kitchen incorporates and utilises stored energy highlights the real-life benefits of energy storage systems, seamlessly blending functionality and sustainability.
Moving further into the house, we find ourselves in the utility area. Here, the air thrums with the quiet power of energy storage systems, balancing the home's temperature through a clever heat pump paired with batteries. These systems allow solar energy to efficiently power the heat pump, which can then be used to keep the house warm or provide hot water, even long after the sun has set.
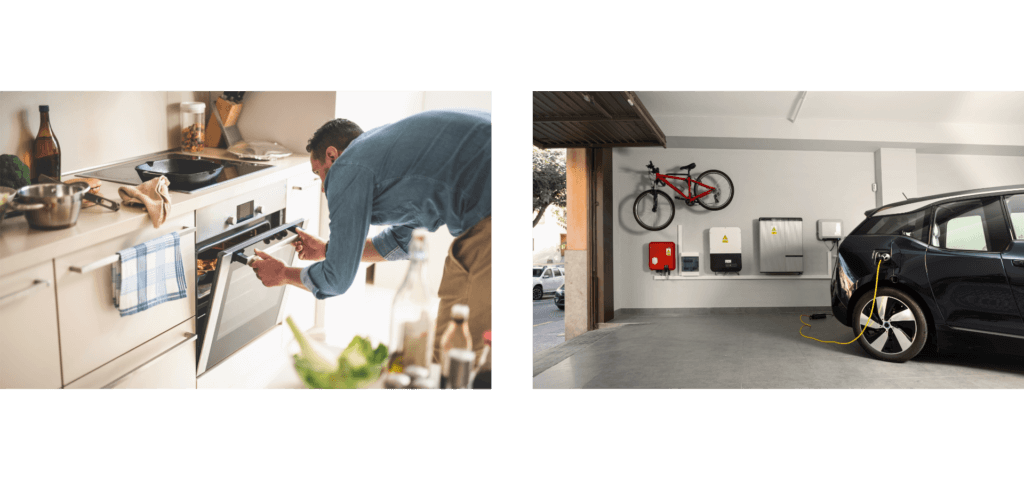

Heading to the garage, the connection between energy management and mobility can be seen in action. An electric vehicle has become an essential part of the home's energy system, quietly charging and preparing for its next journey. Here, the vehicle-to-home power-sharing concept comes to life, allowing energy to flow back into the house during peak times or unexpected outages.
Green future with energy storage
Concluding the journey through the house, we can see energy storage systems integrated into our daily routines as a glimpse into a more sustainable future. From the warm comfort of the living room through the bustling kitchen and out into the garden, we see a snapshot of what could become the norm.
As the European Union strides towards a greener future with initiatives such as the Green Deal, homes equipped with battery energy storage systems are helping us get closer to energy independence. The battery energy storage market is predicted to grow significantly, and all battery technologies will play an important role. In light of the pressing need for climate action, these systems represent vital components of sustainable living and a greener, technologically advanced world.
Uncovering the key role of energy storage in Europe's green revolution
As we step into a new year marked by record-breaking temperatures, the urgency to address climate change intensifies. A recent analysis has confirmed 2023 as the warmest year on record, with over 200 days setting new daily temperature records.
It is crucial that cities join the shared drive to mitigate the climate crisis and transition to greener, more sustainable energy. This was emphasised at COP28, where fossil fuels were officially recognised as the primary cause of climate change for the first time after 28 years. Within Europe, the European Commission is leading the way by introducing ambitious initiatives such as the Fit for 55 package and Effort Sharing Regulation to shift towards a low-carbon economy. These initiatives have sparked innovation and collaboration among European cities as they strive to embrace a more sustainable path.
The second part of our series on sustainable cities highlights the transformative efforts of three European cities – Helsinki, Ljubljana, and Sofia – in embracing energy storage to spearhead their sustainability goals. These cities serve as examples of how local governments can initiate a transition towards renewable energy, sustainable transportation, and emission reduction.

Embracing sustainable energy solutions
In the northern part of Europe, Helsinki is a pioneer in sustainability. The Finnish capital has embraced energy storage as a key element in achieving its goal of carbon neutrality by 2030. The city has launched an inventive project in collaboration with its energy provider to integrate battery energy storage into electric vehicle charging stations. The initiative taps into the potential of electric vehicles as mobile energy storage units, capable of storing excess energy generated from renewable sources. This energy can power the vehicles or be returned to the grid, making the energy ecosystem more connected and resilient.
According to the city's mayor, Juhana Vartianten, building a sustainable future is the most pressing issue we face today. "Helsinki wants to encourage cities around the world to embrace sustainability work and take concrete action. The coming years will determine the direction humanity takes, " said Vartiainen in the 2023 Voluntary Local Review, "That is why we must act now, and we must act together. We still have a long way to go, but fortunately, we are heading in the right direction."
Sofia, the vibrant capital of Bulgaria, is another city that has made sustainability a cornerstone of its urban development strategy. The city has implemented a number of innovative projects that are helping to reduce its reliance on fossil fuels and improve energy efficiency.
One of Sofia's most notable initiatives involves the installation of intelligent batteries throughout the city's public transportation network. These batteries act as mobile energy storage units, allowing buses and trams to store energy while braking or coasting downhill. The captured energy can then power the vehicles as they climb uphill or accelerate. This approach has shown promising results during its trial phase, with an expected 10-15% reduction in fuel usage and a 30% decrease in harmful carbon emissions, contributing to cleaner air and a more sustainable transportation system.
In addition to the environmental benefits, Sofia's battery storage project also streamlines the public transportation system, reducing the need for frequent recharging. The batteries provide a clean source of energy that can be used during peak hours, allowing passengers to rely on a more efficient public transportation system.

Harnessing the power of energy storage
Ljubljana, the capital of Slovenia, is known for its eco-friendliness and sustainable urban development. The city is taking steps to make its buildings sustainable while preserving its rich cultural heritage. One way Ljubljana is achieving this balance is by implementing energy storage systems in public buildings and infrastructure. The Ljubljana City Hall is equipped with a battery storage system that can store energy from the sun. Moreover, Ljubljana aims to expand its energy-saving efforts beyond City Hall by installing energy storage systems in public buildings such as schools, libraries, and other facilities.
Integrating energy storage systems into public buildings is a win-win solution for both cities and citizens. By doing so, the city enhances energy security, lowers energy expenses, and provides backup power during grid outages. This not only reduces the city's environmental footprint, but also provides its citizens with reliable access to energy.
In a world where climate change looms, Helsinki, Ljubljana, and Sofia are examples of how innovation and energy storage can shape a sustainable future. These cities have set the bar high by adopting measures that align with the EU's Green Deal goals, aiming to reduce carbon emissions and switch to renewable energy sources.
Helsinki's electric vehicle charging stations, Ljubljana's public buildings integrated with battery systems, and Sofia's intelligent battery storage for public transportation all show how technology can help create a cleaner, more resilient planet. By reducing carbon emissions and embracing renewable energy sources, these cities are leading the way in the fight against climate change.
Europe’s bold plan for clean air and economic growth
Climate change is unfolding right before our eyes. While discussions surrounding it have persisted for decades, the time for mere discourse has passed. This year, we saw Arctic sea ice hit record lows during winter, endangering polar wildlife and accelerating global warming. In contrast to the ice decline, Europe experienced devastating floods in many countries. Heavy rains and high river levels caused widespread flooding, affecting communities and infrastructure. These are not isolated incidents but signs that our planet is in distress. It is now crucial to translate words into action. That's precisely where the European Commission’s Fit for 55 package takes the stage. As a vital part of the EU's Green Deal, this visionary plan is strategically crafted to tackle the pressing challenges of climate change. Its main objective is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in the European Union by at least 55% by 2030. As the world heats up and our environment gets sadly more unpredictable, Fit for 55 steers towards a greener, more sustainable future.
At the heart of this change is energy storage. In the context of the Fit for 55 package, there are several reasons highlighting its importance. Energy storage fuels the transition to environmentally friendly transportation and green mobility. This is possible through innovations like smart grids and battery systems powering electric buses in urban areas. Such integration of energy storage with public transportation not only reduces emissions but also makes green mobility accessible. Energy storage opens up job opportunities and boosts local communities. Furthermore, it is crucial in making energy more affordable, offering a safety net for those grappling with rising energy costs.
Driving the energy transition
As a result of the Fit for 55 initiative, energy storage operates on three essential fronts: improving air quality, generating job opportunities, and stabilising energy prices.
Air pollution is a serious problem affecting millions of people around the world. It can cause respiratory problems, heart disease, and cancer. Improving air quality is one of the key goals of the Fit for 55 package. It sets a bold target: zero emissions from new cars and vans by 2035. Energy storage is a vital driver in this journey to reduced air pollution and eco-friendly mobility.
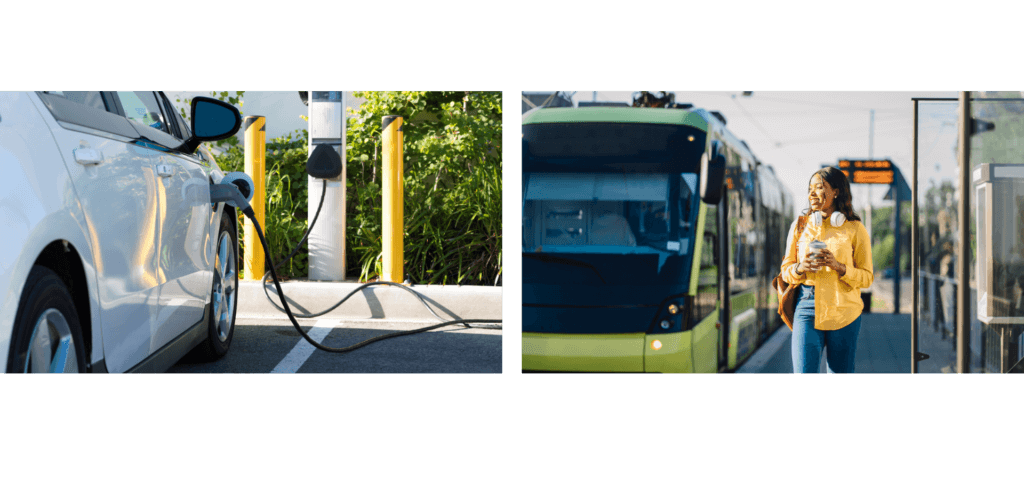

Electric cars are the ambassadors of emission-free transport, and energy storage has the ability to power them. Energy storage also provides backup power for charging stations, ensuring that electric car owners can always find a place to recharge. Electric cars produce fewer emissions than traditional diesel-powered cars, and increasing their use helps to improve air quality. It is a stride towards a future defined by greener travel, with less smog and more fresh, clean air.
Cities and towns all over Europe are tapping into the potential of energy storage, harnessing electricity from renewable sources like the sun and wind. This stored energy fuels the urban transit networks, providing a lifeline to buses and trams. The result? A sharp decline in air pollution, quieter streets, and reduced reliance on fossil fuels. Energy storage acts as a safety net for electric buses and trains, improving the resilience and reliability of public transportation systems. In the event of a power outage, energy storage can provide backup power, ensuring that the city's transport continues to operate. Energy storage becomes an indispensable sidekick as the world shifts towards green transportation, creating a healthier environment.
Added to the industrial new development, there is another aspect of European’s stagnating and lasting issue: high employment rates. The job market is evolving unprecedentedly, leaving job seekers and employers grappling with new challenges and opportunities. As the global appetite for renewable energy grows, so does the demand for a diverse and skilled workforce. The Fit for 55 package aims to create more job opportunities within the clean energy sector. Energy storage, among other clean energy solutions, calls for an array of professionals, from engineers and technicians to electricians and software developers.
When an energy storage company establishes a new factory in a rural area, it does not only bring job opportunities to the community but also stimulates the local economy. The ripple effect is significant, as various services are required to support the factory. Construction workers, transportation services, and material suppliers all benefit from the newfound wave of activity. This synergy, driven in no small part by energy storage, highlights the potential of clean energy to power our homes, livelihoods, and economies.
Affordable energy is a pressing concern for communities and individuals globally. The COVID-19 pandemic and the war in Ukraine have aggravated the energy crisis, pushing energy prices to record highs. This is having a devastating impact on people and businesses, particularly those who are already struggling to make ends meet. The Fit for 55 package seeks to make energy more wallet-friendly for everyone, and energy storage is central to this vision.
Energy storage allows storing electricity during quiet hours when it's less expensive and tapping into these reserves when electricity prices skyrocket during peak demand. It's akin to purchasing energy at a discount rate and seeing savings grow.
Energy storage fosters self-reliance, particularly in regions prone to power hiccups or environmental concerns. Community solar initiatives, often supported by energy storage, are expanding access to solar energy, cutting the cords to the traditional power grid. This approach delivers a double victory, benefiting our finances and the planet's well-being.
Integrating an energy storage system for homeowners with solar panels complies with having a personal vault for energy. During the day, the excess energy is safely stored away. This energy is later used to lighten homes without sending electricity bills soaring. Energy storage systems are transforming the energy landscape, addressing the energy affordability crisis and making it more accessible for everyone.

Towards a greener future
While the Fit for 55 package may initially seem like a distant, abstract concept, its impact is already spreading through our daily lives. Together with energy storage, this visionary strategy has the potential to redefine our homes, our cities, and our communities. Energy storage fuels the shift to environmentally friendly transportation, cleansing the streets and reducing our dependence on fossil fuels. Energy storage solutions create job opportunities, uplift local communities, and place affordable energy within reach.
When the Fit for 55 package and energy storage team up, they have the potential to transform societies, reshape our relationship with the environment, and pave the way for a greener, more sustainable world.
Uncovering the key role of energy storage in Europe's green revolution
In the scorching summer of 2023, Europe was gripping an unprecedented heatwave. This extreme weather triggered a series of devastating events, including wildfires raging through Southern France and droughts that left the water reservoirs in Spain critically low. Such disasters were a stark reminder of the pressing need to address climate change head-on, an undeniable call to action.
In response, the European Commission and the cities across the continent have united, propelling Europe toward a more environmentally conscious future. At the core of this collective effort lies the Effort Sharing Regulation, which assigns emission reduction targets to each member state. With their sights firmly set on these targets and a dedicated commitment to combat emissions, European cities are charting a course towards sustainability, driven by innovation and a shared vision of a greener tomorrow.
This article explores three local initiatives - Copenhagen’s and Barcelona’s Climate plans and Tallinn as Europe’s Green Capital. Together, they exemplify how cities actively invest in renewable energy, advocate for sustainable transportation, and advance emission reduction. What unites these cities is their reliance on energy storage, with batteries emerging as integral components within these systems.
A green wave all over Europe
In the heart of Catalonia, Barcelona takes a bold stance in Europe’s ongoing battle against climate change. The city’s Climate plan sets a clear course towards reducing emissions and embracing renewable energy. At the forefront of this environmental mission are energy storage systems, with time-tested batteries powering businesses and homes across the city.
Barcelona’s first energy community epitomises this shift. Along the bustling Barcelona Port, solar panels soak in radiant Mediterranean sun. What sets this community apart is its ability to capture excess solar energy, preventing it from going to waste. Instead, it’s harnessed by energy storage systems. This stored energy becomes a precious resource, fueling essential port operations, from lighting to refrigeration. The Barcelona Port stands as an exemplary testament to the transformative potential of energy storage, pushing the city toward its climate goals one watt at a time.

Copenhagen has set an ambitious goal: to become the world’s first carbon-neutral capital by 2050, as outlined in its Climate plan. This visionary concept encompasses many initiatives, all connected by a central theme, energy storage.
A standout feature of the plan is Copenhagen’s extensive electric bus fleet, powered by battery energy storage systems. These systems store the energy that propels emission-free buses along the city’s bustling streets. In 2021, Copenhagen made waves by introducing 100 electric buses, to reduce annual greenhouse emissions by 5,000 tons. The city’s vision stretches even further, anticipating 50,000 electric vehicles on its roads by 2025, with advanced energy storage technologies seamlessly integrating modernity into urban life.
Copenhagen’s Climate plan encompasses initiatives ranging from retrofitting buildings with energy-efficient technologies to harnessing wind turbines and photovoltaic systems. In this vibrant metropolis, we witness the potential that arises from the marriage of renewable energy and energy storage solutions.
One of Europe's greenest cities is Tallinn. This progressive city with mediaeval charm was honoured with the European Green Capital 2023 title, recognising its ambitious sustainability plans. To achieve carbon neutrality, Tallinn is making substantial investments in renewable energy and energy-efficient initiatives. The city’s strategic approach to sustainability hinges on energy storage and the development of a smart grid, using digital technology to manage the flow of electricity.
A shining example of Tallinn’s commitment to energy storage is Ülemiste City Energy Storage Park. A robust energy storage system is nested within the park, ensuring no clean energy goes to waste. The park reduces the city's dependence on polluting fossil fuels and paves the way for increased local clean energy generation.
Tallinn’s mayor, Mihhail Kõlvart, firmly believes cities will be crucial in achieving European climate and sustainability targets. “European Green Capitals need to take leadership in creating sustainable, resilient and inclusive cities of the future to ensure a high-quality living environment,” stated Kõlvart, emphasising the value of collaboration among cities.

A sustainable energy storage transition
These local initiatives showcase the proactive spirit of European cities in the battle against climate change. In their stories, energy storage is a bridge connecting renewable energy to our daily lives. In Copenhagen, energy storage ensures swift and modern public transportation. In Tallinn, it fuels the city’s green revolution. In Barcelona, it keeps the bustling port community in motion.
With their progressive climate plans, these cities remind us of the importance of energy storage and its role in achieving the goals set by the Effort Sharing Regulation and the European Green Deal. By hopping on the energy storage bandwagon, cities across Europe are speeding toward a sustainable and low-carbon future.
As part of CBI’s technical team, we’ve recently welcomed Begüm Bozkaya. With a BSc degree in Chemistry from the Middle East Technical University and an MSc degree in Materials Science from the Technical University of Munich, she gained extensive knowledge on the effects of carbon additives on negative plates for lead batteries, after using this as a Ph.D. research topic.
After working on several industrial projects for the past 6 years, Begüm joined CBI to gain a broader perspective on lead battery research as her role involves directly working with CBI’s global members from different companies and stages of the supply chain. She will be managing all of CBI’s European Technical projects as well as supporting CBI’s standards program.
According to her, CBI is doing what no one else in the industry is by “combining the knowledge from the industry and research institutes and collecting them in a non-competitive environment”. This means it’s possible to pool knowledge from a range of battery experts in order to advance lead battery technology for all applications, from energy storage systems to automotive.
As part of CBI’s team based in Europe, it is also important to look at the role of EU industry-research-academia partnerships in driving innovation. “We need to strongly defend the place of lead batteries. This is a well-established technology: we are cost-effective, recyclable, we have innovative research initiatives underway, and we’re committed to contributing to a cleaner future in the energy sector, especially to facilitate decarbonisation and support climate goals. It is vital that the EU includes all batteries in their future work plans”.
In that sense, the work developed by CBI through its Technical Roadmap has been essential to collect relevant information for lead battery applications and to help educate the audience regarding the future of this technology that has an enormous potential:
“If we can open new research topics and innovative ideas that can cover what we have in the roadmap, I’m sure lead batteries can still be considered a key player in the efforts to decarbonise, and developed further as a result. Research is the key point.”

When mentioning the new year and the developments that we can expect from advanced lead batteries, Bozkaya said that bipolar or advanced PbC batteries “can bring new research topics” for the industry and that these are “great candidates for EU initiatives”:
“There’s a bright future for advanced lead batteries and a lot of great research projects being developed as a result of CBI’s work, so I believe that in the near future we will be able to show even more how committed the industry is to Europe’s climate goals and, therefore be more involved with EU initiatives through lead battery research projects”.
For more information on CBI’s innovative technical program, click here.
On October 4, CBI brought together a digital panel to discuss the critical role of batteries for Europe’s sustainable transition. As part of Europe's Sustainable Energy Week, supported by the EU Commission, the virtual event provided an open discussion around the importance of a level playing field amongst technologies in Europe and featured European case studies where advanced lead batteries are providing reliable, recyclable and safe energy storage.
CBI’s Research and Innovation Manager, Dr Carl Telford, opened the event by showcasing our recently launched Technical Roadmap, to illustrate that “sustainable economies need batteries”. If policy makers want to solve the problems of climate change and pollution, while moving from a linear to a circular economy, then industries will “need a proper deployment of battery technologies and energy storage”, and this is where Europe’s lead battery industry plays a key role.
From Exide Europe, Holger Fricke, Director Basic Research R&D EMEA, presented the benefits of Exide’s “on-site solar installation in Portugal”, that combines lead battery energy storage with renewable energy. Carbon emissions were reduced by more than 20% and energy management was improved, turning this case study into a real-world example of decarbonisation, with the installation facilities now being used as a showcase.
Peter Stevenson, Senior Technical Co-ordinator at GS Yuasa, joined the event to discuss the importance of hybrid solutions for Europe’s sustainable energy future. Using an example of the “world’s first container of dual chemistry energy storage system”, he highlighted the “complementarity and flexibility” between lead and lithium battery technologies.
While moderating the panel, Patrick Clerens, Secretary-General at EASE, reflected on the need of a level playing field between different technologies and stated that “no one can pick a technology winner”. Europe needs more batteries and new battery technologies, including hybrid ones, and through this it is possible to have “the best of both worlds”.
There are already some EU industrial and research initiatives going on to demonstrate how batteries can work together to reach the energy demands, such as the European Battery Alliance, Batteries Europe, Batteries 2030+ or IPCEI's. However, it remains important to share the message that a wide array of energy storage and battery technologies are needed to address the flexibility requirements and support the energy transition and the EU green goals, including lead batteries.
By the end of the discussion, it was clear that other industries can learn from the lead battery experience since it’s a well-established industry that represents a major example of circularity in Europe. Through research and innovation, enhancing the performance of lead-based technologies will be essential for Europe’s sustainable energy future and create further opportunities for synergies with other chemistries.
Watch the video of the event:
Download the presentations from the event below:
On September 15, the EU Commission’s President made a State of the Union speech highly focused on the future: from investing in 5G, to improving research and innovation and making sure that Europe will reach the EU Green Deal goals. Ursula Von der Leyen pointed out some of the key aspects that rule our work at CBI and our dialogue with our members and companies from the industry.
Through NextGenerationEU, the Commission is committed to “invest in 5G and digital skills” as the demand for faster and more efficient networks increases, along with the explosion of AI, EVs and many other real-time autonomous applications.
“To ensure uninterrupted access to these services, telecoms and data centre back-up demand will increase exponentially” and this is where lead batteries have an important role. As the main option for the “uninterruptible power supply (UPS) energy storage needed for data centres and network rooms” representing 90% of global demand, lead batteries are a critical player for Europe’s digital transition.
But let’s not forget about the role of this technology for hospital back-up applications, incredibly relevant during the COVID-19 pandemic, by “ensuring uninterrupted power supplies”. In Italy and in the UK, FIAMM’s provided safe and reliable lead batteries to support hospital power.
Another wish from Von der Leyen is to achieve “European tech sovereignty”, which also includes the ability to supply the entire value chain in many highly demanded technologies, such as EVs, hybrid vehicles or renewable energy storage systems. CBI recognizes that all batteries are needed to give Europe the faculty to attain green goals and, as we invest in research and innovation for advanced lead batteries and work with world-class institutes, we are here to say that this technology is a critical player in the green transition by offering “high-performance, reliability, safety and a sustainability profile including almost 100% recycling at end-of-life in Europe”.
We are demonstrating that lead batteries can make EVs safer, that our members are involved in clean energy storage projects contributing to decarbonization and that this technology is a great team player when collaborating with other batteries and using the best of both chemistries for a more efficient outcome.
As the urge for a fair green transition and a cleaner energy society increases, CBI believes that the actions to reach 2030 goals must be taken now and that the potential and opportunities for advanced lead batteries are limitless:
